The Stochastic indicator is a popular momentum indicator that can significantly improve your Forex trading when combined with other techniques.
By aligning Stochastic signals with trend analysis, you can confirm the strength of prevailing market directions and filter out false signals.
Additionally, validating Stochastic signals with Japanese candlestick patterns and chart patterns provides additional confirmation signals, increasing the precision of trade setups.
Moreover, considering Stochastic conditions near significant support and resistance levels offers valuable insights into potential reversal or breakout points in the market.
How Does the Stochastic Indicator Work?
The Stochastic Indicator operates on the premise that closing prices accumulate near the upper end of the price range as an uptrend progresses, signaling strength.
Conversely, during a downtrend, prices gravitate towards the lower end of the range, indicating weakness.
The Stochastic Indicator visually represents this phenomenon by comparing the current closing price to the highest high and lowest low over a specified period.
The default Stochastic settings are:
- %K Length = 14
- %K Smoothing = 1
- %D Smoothing = 3.
However, these settings are susceptible to false signals.
The Slow Stochastic settings are more popular:
- %K Length = 5
- %K Smoothing = 3
- %D Smoothing = 3
The Slow Stochastic settings are used in the examples below.
%K Line
The %K line represents the current closing price’s position relative to the highest high and lowest low over a set period.
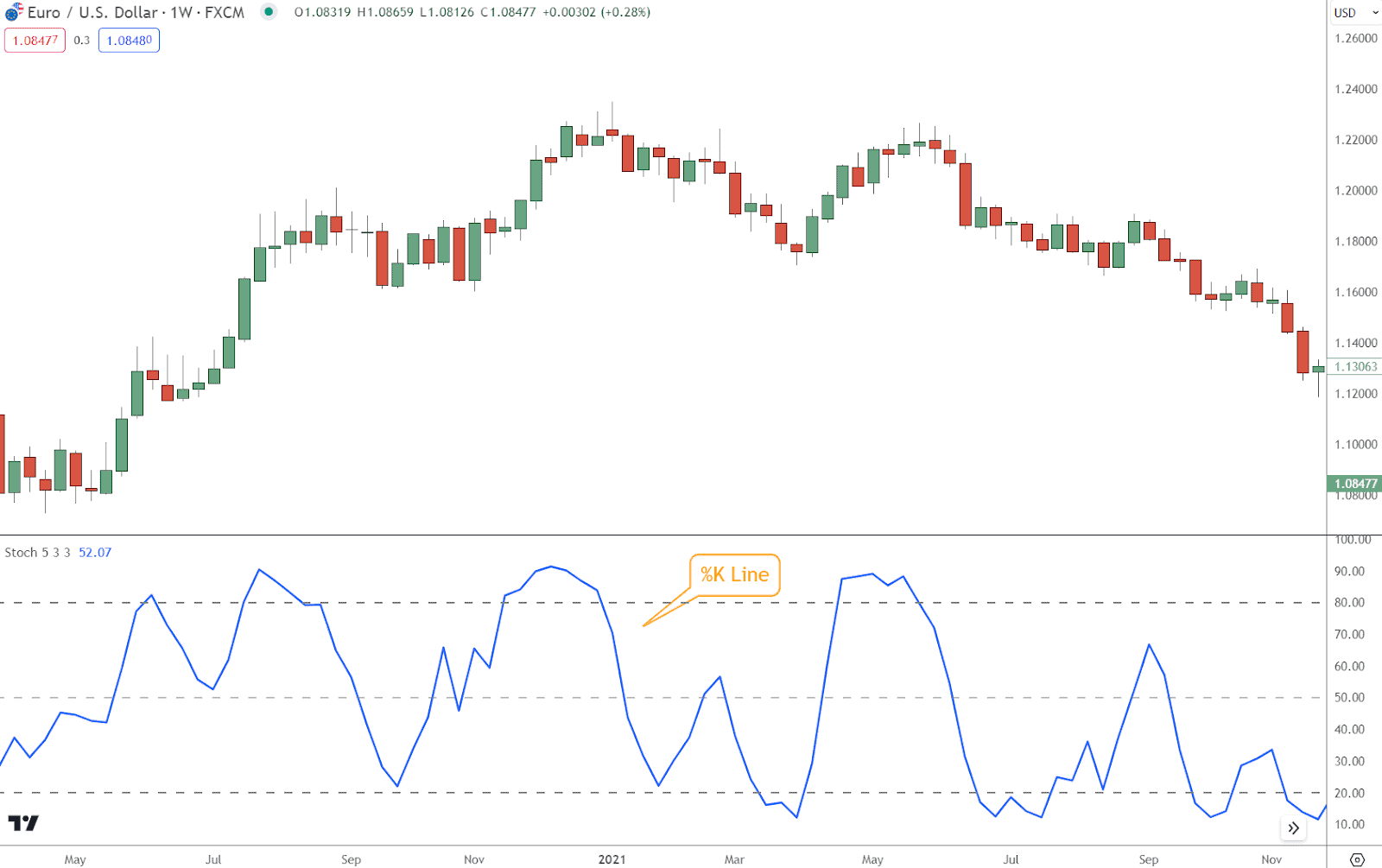
One calculates it mathematically:

This formula generates values between 0 and 100, with higher values indicating that the closing price is closer to the highest, signifying bullish momentum.
Lower values suggest proximity to the lowest low, signaling bearish sentiment.
%D Line
The %D line is a moving average of the %K line and appears smoother on the indicator chart.
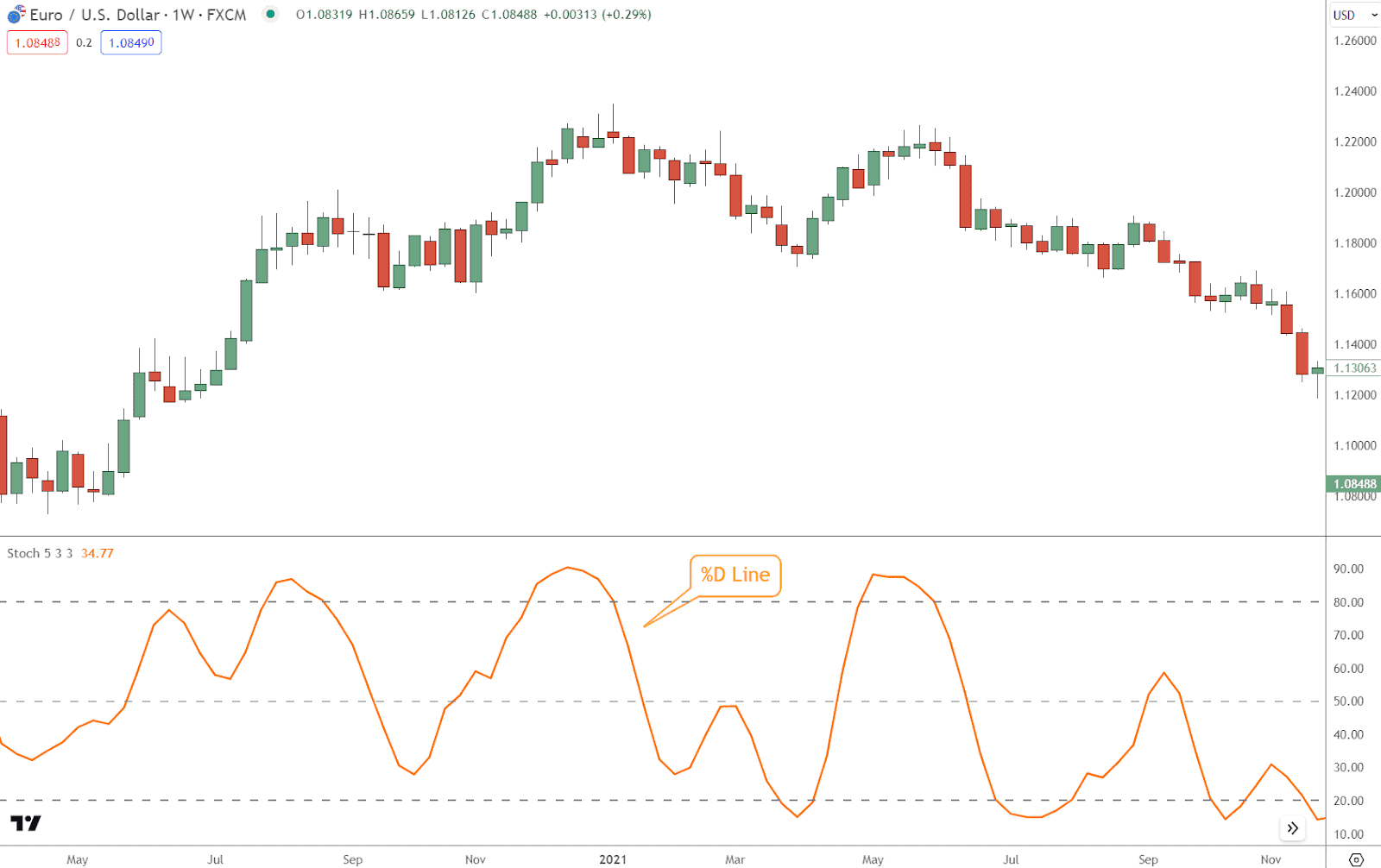
It helps to filter out short-term fluctuations and provides a clearer picture of momentum shifts.
How to Interpret Stochastic Indicator Signals?
Interpreting Stochastic signals is fundamental to leveraging this indicator effectively in Forex trading.
By understanding the various signals the Stochastic indicator generates, you can make informed decisions and capitalize on market opportunities more precisely.
Overbought and Oversold Conditions
Identifying overbought and oversold conditions is one of the indicator’s primary functions.
These conditions provide insights into potential exhaustion points in the market, offering valuable cues for traders.
- Overbought Conditions: Buying pressure intensified significantly when the Stochastic Indicator’s readings surged above the 80% threshold.
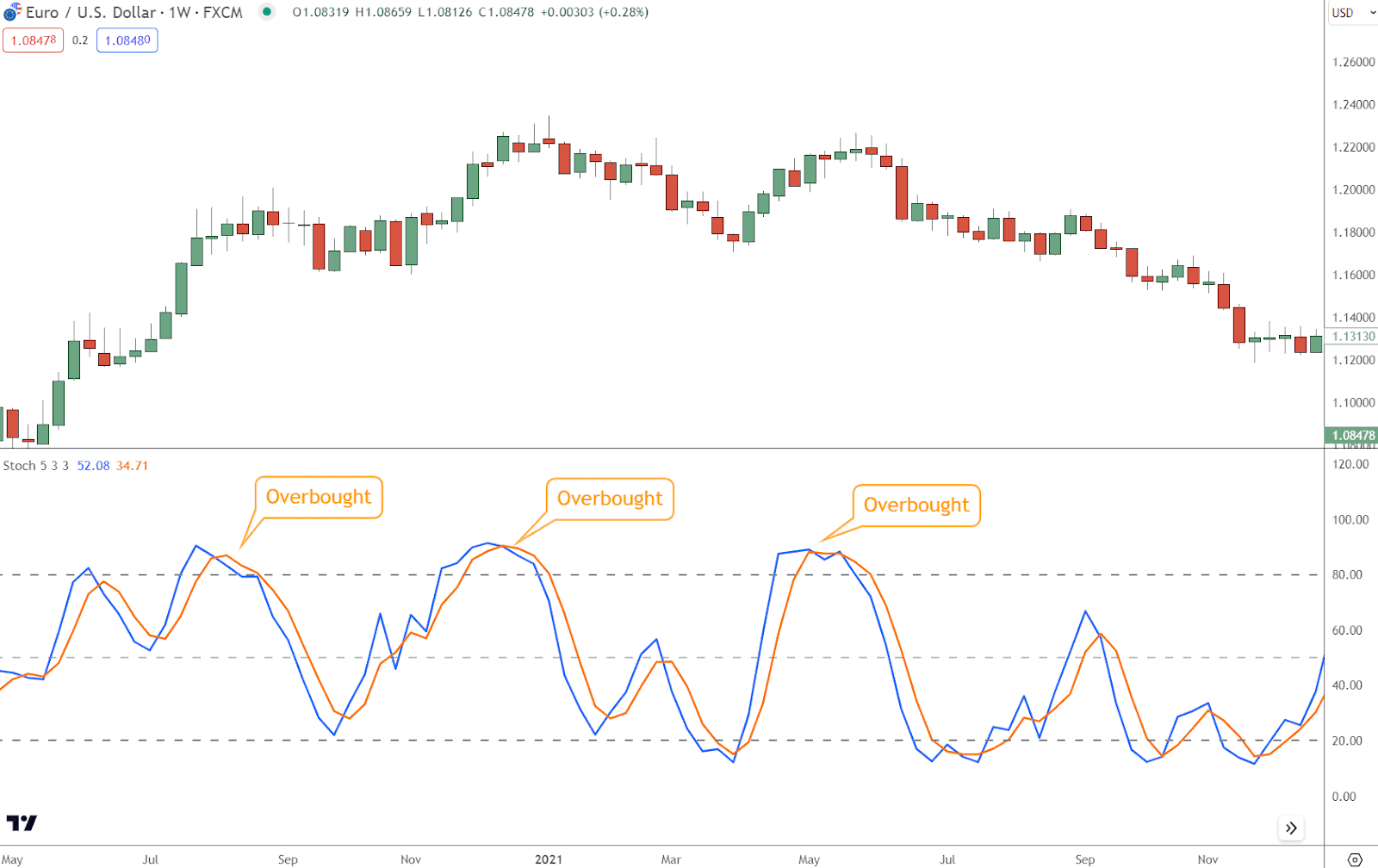
This condition suggests that the market may be overbought, and a price reversal or corrective pullback could be imminent.
View overbought conditions as opportunities to consider taking profits on long positions or potentially initiating short positions.
- Oversold Conditions: Selling pressure intensified substantially when the Stochastic Indicator’s readings plummeted below the 20% threshold.
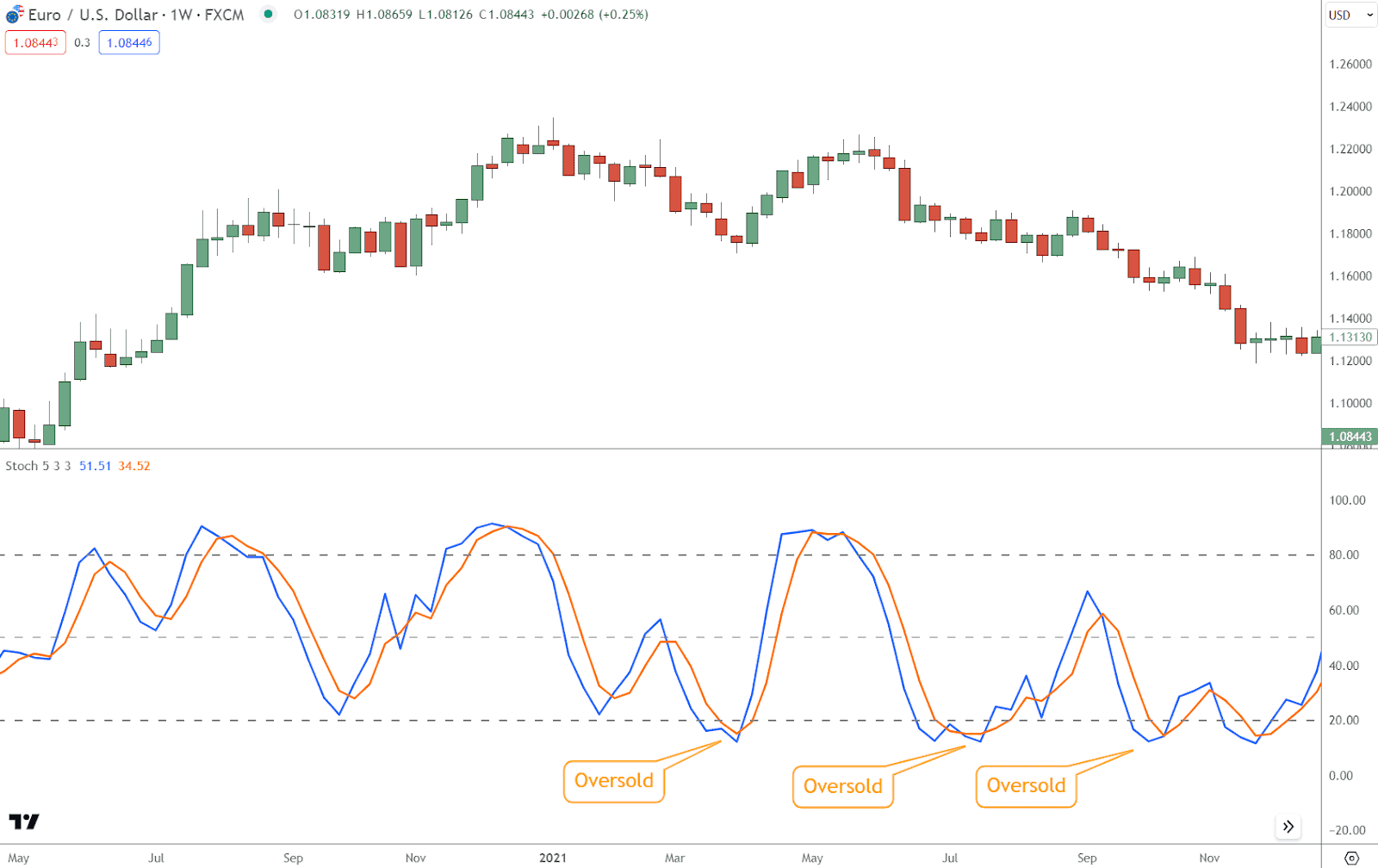
This condition indicates that the market may be oversold, and a price rebound or reversal could be on the horizon.
Interpret oversold conditions as potential opportunities to enter long positions or tighten stop-loss orders on existing short positions.
Signal Line Crosses
The signal line crosses play a pivotal role in Stochastic analysis, providing clear indications of shifts in market momentum.
- Bullish Signal: When the %K line crosses above the %D line, it generates a bullish signal. This crossover suggests that buying pressure is strengthening, potentially leading to upward price movements.
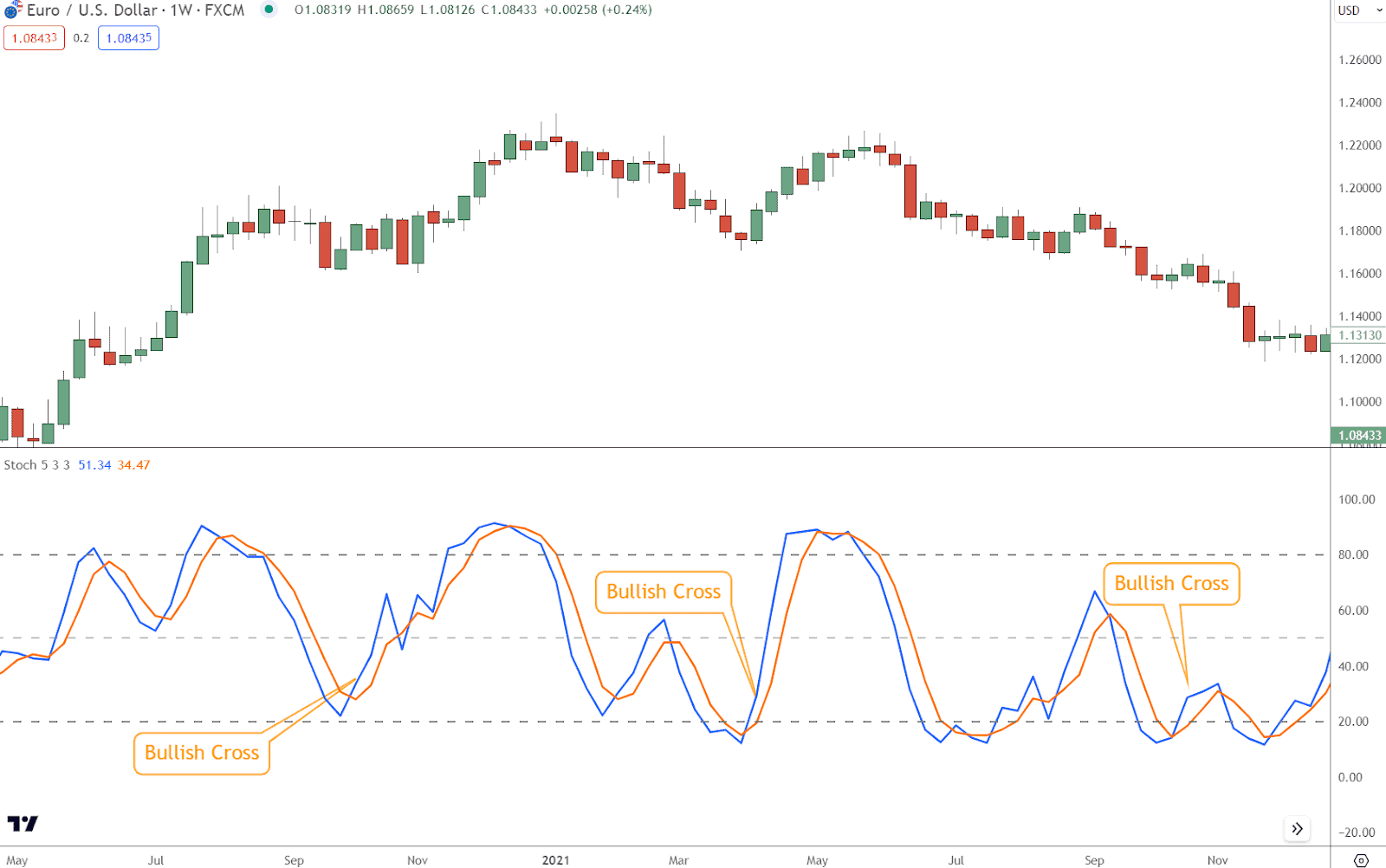
Interpret bullish signal line crosses as opportunities to enter long positions or add to existing ones, anticipating continued upward momentum.
- Bearish Signal: Conversely, a bearish signal occurs when the %K line crosses below the %D line. This crossover indicates that selling pressure intensifies, signaling a potential price downturn.
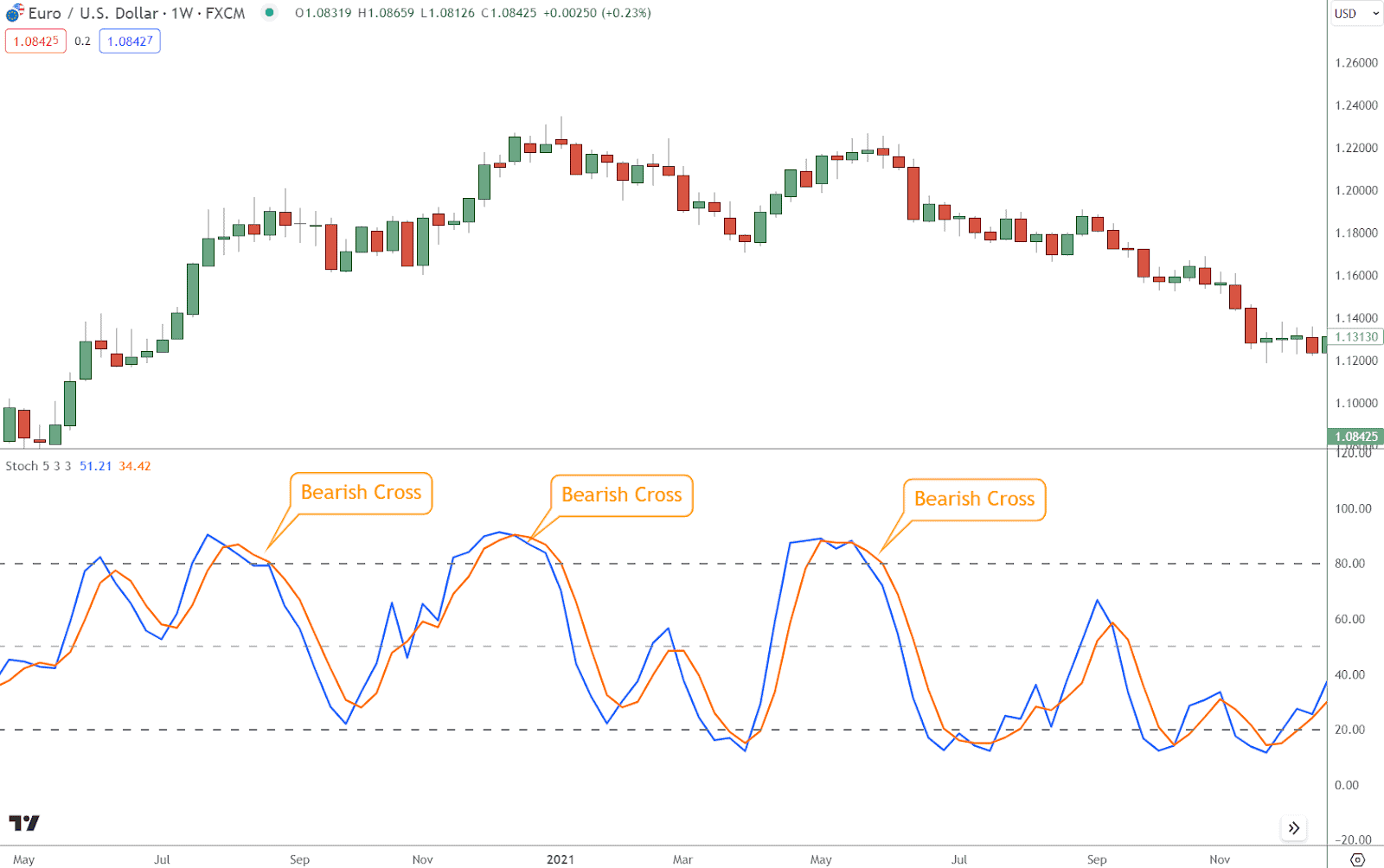
Interpret bearish signal line crosses as opportunities to enter short positions or tighten stop-loss orders on existing long positions to protect profits.
Divergence
The divergence between price action and the indicator can offer valuable insights into potential trend reversals.
- Bullish Divergence: Bullish divergence occurs when prices form lower lows while the Stochastic indicator forms higher lows.
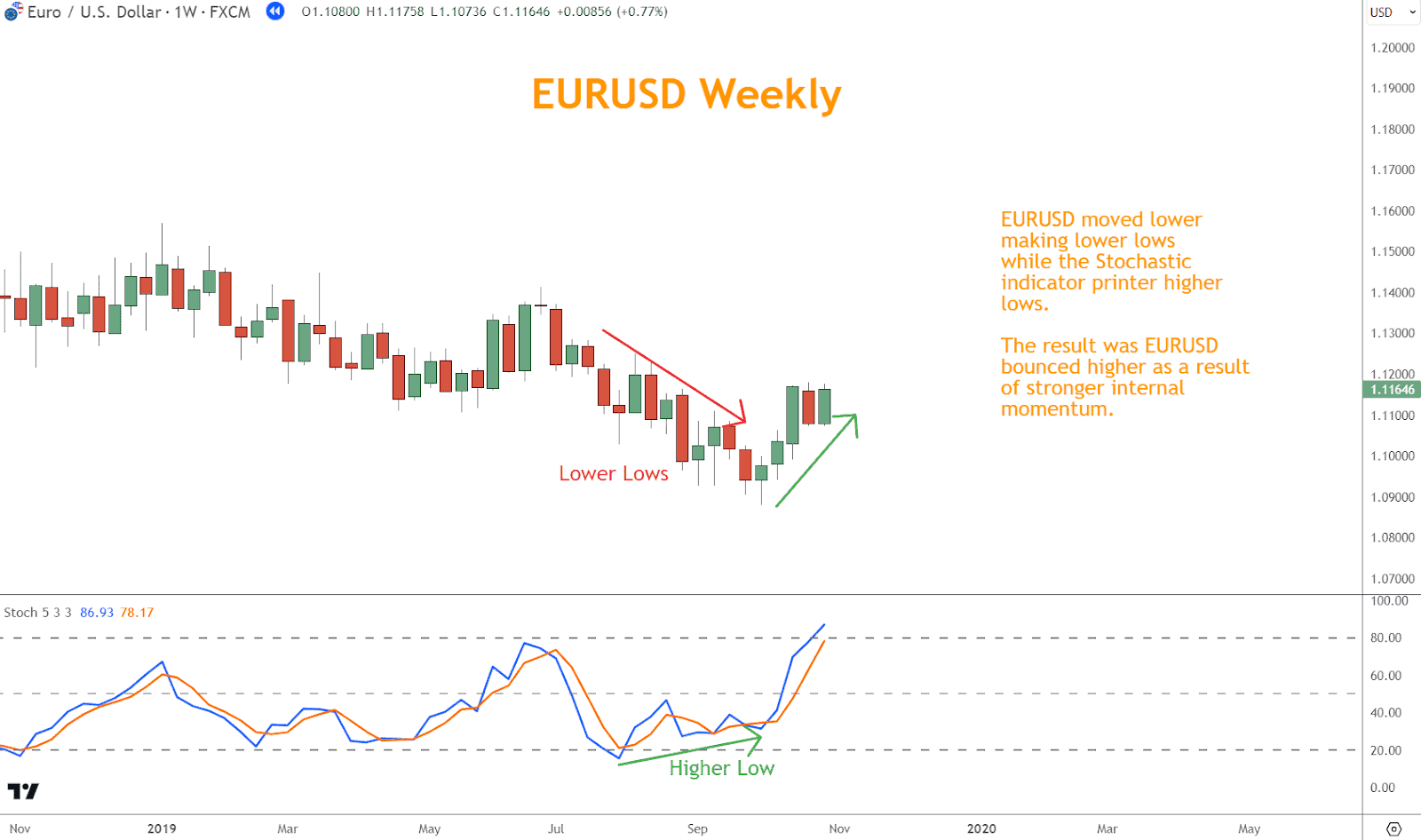
This condition suggests that although prices are declining, momentum is beginning to shift upwards.
Interpret bullish divergence as a potential precursor to a bullish reversal, considering it an opportunity to enter long positions or tighten stop-loss orders on short positions.
- Bearish Divergence: Conversely, bearish divergence occurs when prices form higher highs while the Stochastic Indicator forms lower highs.
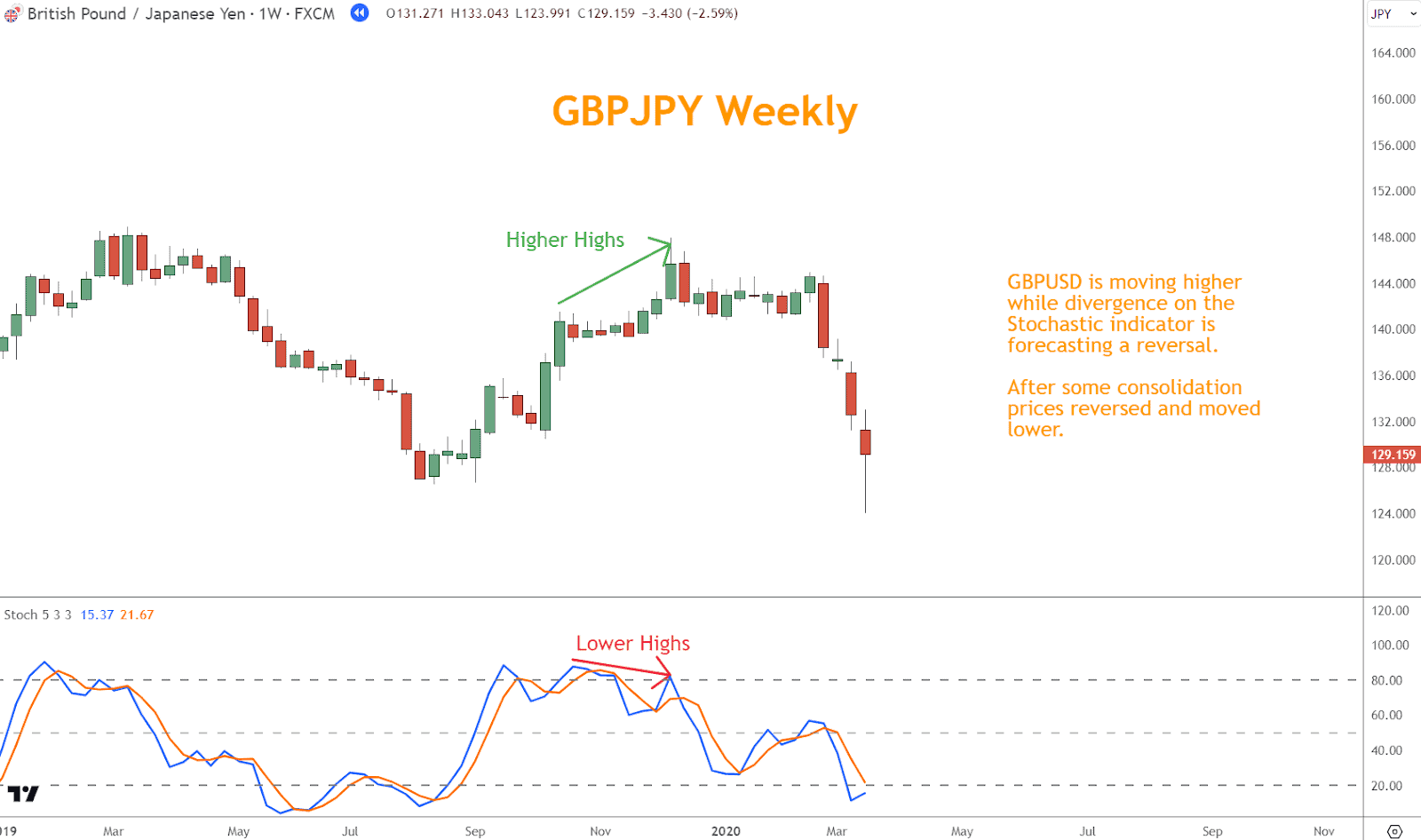
This condition indicates that despite rising prices, momentum is weakening.
View bearish divergence as a warning sign for a bearish reversal, considering it an opportunity to enter short positions or tighten stop-losses on long positions.
How to Integrate the Stochastic Indicator with Other Tools
Combining it with other essential tools and indicators can significantly enhance its effectiveness in Forex trading.
By integrating Stochastic analysis with complementary techniques, you can gain deeper insights into market dynamics and improve the accuracy of your trading decisions.
Trend Analysis
Incorporating Stochastic analysis into trend analysis can provide valuable confirmation signals and filter out false signals.
Aligning Stochastic signals with the prevailing trend increases their reliability and strengthens trading strategies.
- Uptrend: In an uptrend, traders focus on oversold conditions identified by the Stochastic Indicator as potential entry points for long positions.
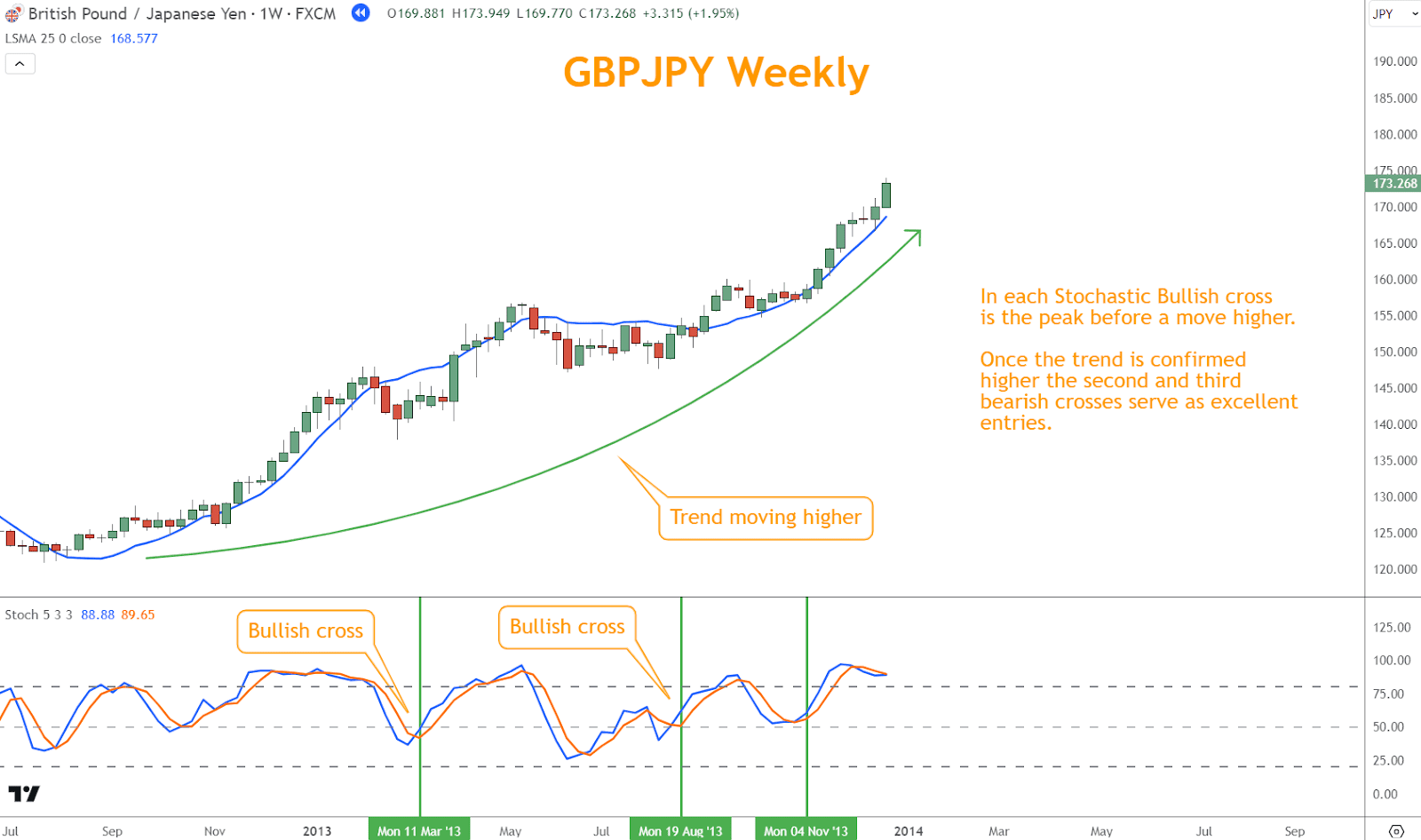
When Stochastic readings reach oversold levels (below 20%) and align with the uptrend, it signals a high-probability buying opportunity.
This convergence of signals reinforces the likelihood of successful trades.
- Downtrend: Prioritize overbought conditions identified by the Stochastic Indicator as potential entry points for short positions in a downtrend.
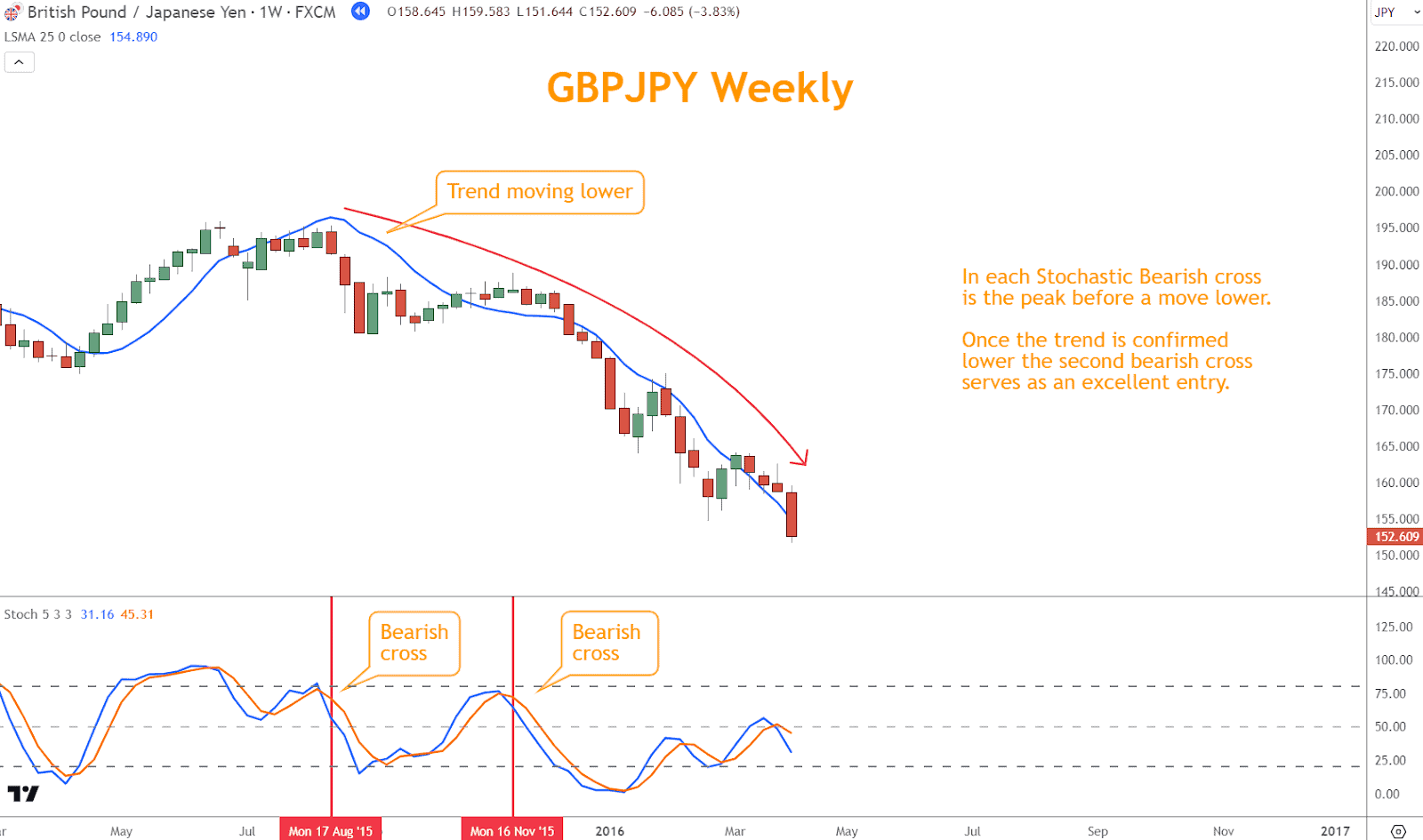
In the example above, the confirmed selloff creates opportunities each time the bearish cross on the Stochastic indicator appears.
Confirming Stochastic signals with the prevailing trend minimizes trading risk against the predominant market direction.
Japanese Candlesticks and Chart Patterns
Integrating Stochastic analysis with Japanese candlestick patterns and chart patterns enhances the precision of trade setups and provides additional confirmation signals.
- Candlestick Patterns: You can validate Stochastic signals with common candlestick patterns such as Bullish Engulfing, Hammers, or Morning Star reversals.
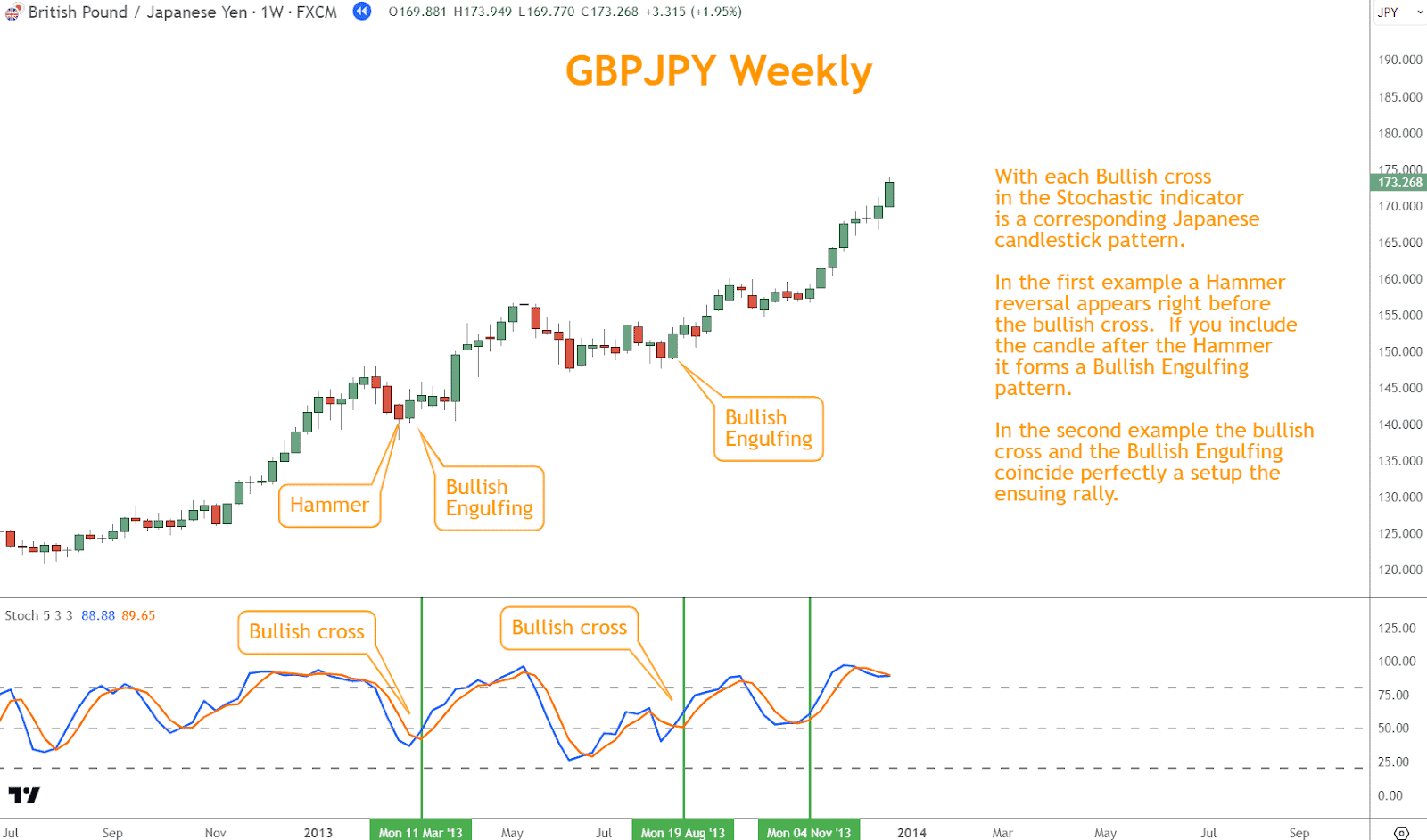
With each Bullish cross in the Stochastic indicator is a corresponding Japanese candlestick pattern, as seen in the example above.
In the first instance, a Hammer reversal appears before the bullish cross. If you include
the candle after the Hammer, it forms a Bullish Engulfing pattern.
In the second instance, the bullish cross and the Bullish Engulfing coincide perfectly to set up the ensuing rally.
- Chart Patterns: You can use double tops, double bottoms, head and shoulders, or triangles to confirm stochastic indicator signals.

In the example above, GBPJPY moved higher, forming a Bearish Rising Wedge whose peak coincided with the bearish cross on the indicator.
When Stochastic crossover conditions coincide with the formation of a chart pattern, it reinforces the likelihood of a significant price movement in the direction indicated by the pattern.
Support and Resistance
Integrating Stochastic analysis with support and resistance levels provides valuable insights into potential reversal or breakout points in the market.
- Support Levels: Stochastic oversold conditions near crucial support levels suggest potential exhaustion of selling pressure and a higher probability of a price rebound.
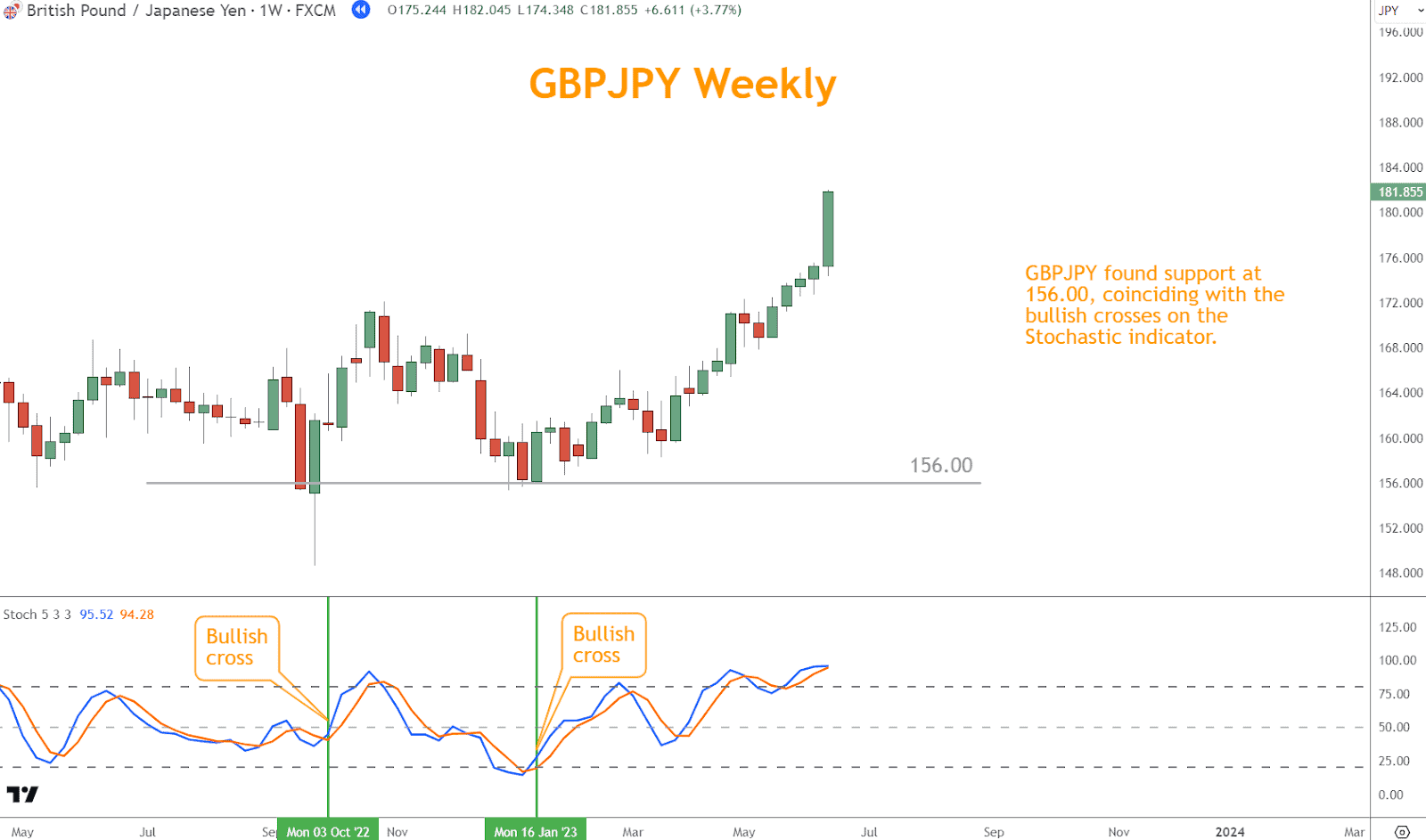
GBPJPY found support at 156.00, coinciding with the bullish crosses on the Stochastic indicator.
- Resistance Levels: Stochastic overbought conditions near significant resistance levels indicate potential exhaustion of buying pressure and a higher probability of a price pullback.
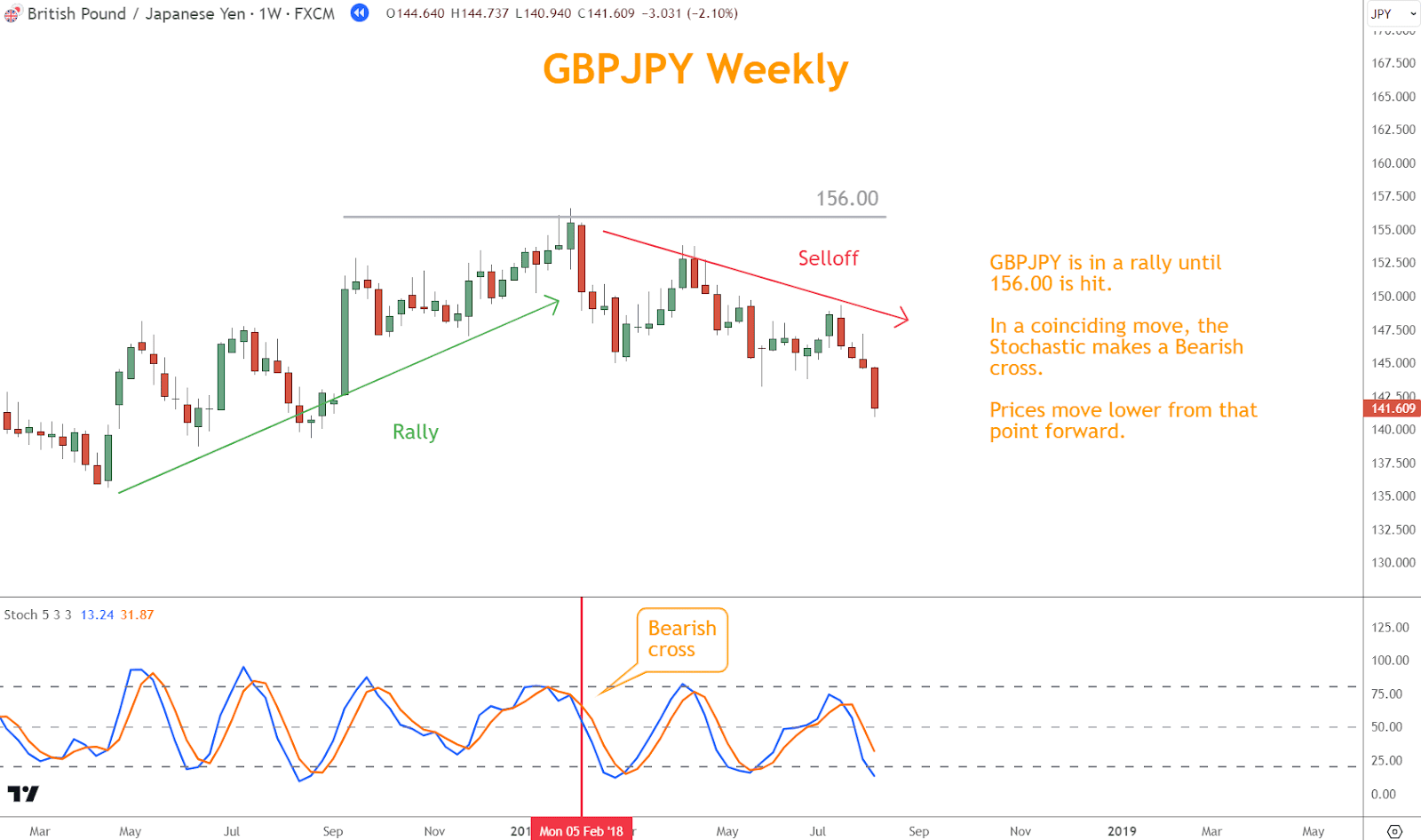
In the above example, GBPJPY rallies until 156.00. is hit. In a coinciding move, the Stochastic makes a Bearish cross.
Prices move lower from that point forward.
By integrating Stochastic analysis with trend analysis, Japanese candlesticks, chart patterns, and support/resistance levels, traders can synthesize multiple sources of information to make more informed trading decisions.
This holistic approach minimizes the risk of false signals and enhances the accuracy of trade setups, ultimately leading to improved trading performance and profitability.
What Problems or Limitations Are There With the Stochastic Indicator?
While the Stochastic Indicator is a valuable tool for identifying overbought and oversold conditions and potential trend reversals in the forex market, it also has limitations.
One of the primary issues is its tendency to generate false signals, especially during ranging or choppy market conditions.
You may experience whipsaws, where the indicator generates multiple conflicting signals, leading to losses or missed opportunities.
Additionally, it may perform poorly in strongly trending markets, as it tends to remain in overbought or oversold territory for extended periods, potentially causing traders to miss out on profitable trades.
While the Stochastic Indicator can be a valuable tool in your arsenal, it is essential to recognize its limitations and use it with other forms of analysis for more robust trading decisions.
Conclusion
The Stochastic Indicator is a valuable tool for Forex traders, offering insights into market momentum and potential reversal points.
Other tools, such as trend analysis, Japanese candlesticks, chart patterns, and support/resistance levels, greatly enhance its efficacy.
However, it’s essential to remember that no single indicator guarantees success.
Combining multiple tools and prudent risk management are necessary for achieving consistent profitability in Forex trading.
What’s the Next Step?
Use this article to look at your favorite charts and determine whether the Stochastic indicator can help your trading strategy.
In addition, look for opportunities to use what you’ve learned in your process.
If you need help developing an analysis process, you can use our Six Basics of Chart Analysis. If you’re unfamiliar with the Six Basics, you can learn them here for free.
The “Six Basics” will give you a strong foundation in chart analysis, which you can incorporate with what you’ve learned about the Stochastic indicator in Forex.
In addition, when you get the “Six Basics,” you’ll also get Forex Forecast delivered to your inbox every Sunday.
Forex Forecast includes:
- Trade Ideas and Analysis
- I will show you the trade opportunities I’m watching using the Six Basics of Chart Analysis and Advanced Strategies.
- Case Studies from Around the Web
- Watch how applying the Six Basics worked on some of the best, most profitable trades.
- Trading Education Guides and Videos
- Want to learn most Six Basics techniques and advanced strategies?
- I produce Videos and Guides to help you learn and build a better trading practice.
- Links to New Articles
- I publish new articles on topics traders will want to know about every week, and you can find out when they post.
- Positionforex.com News
- Did something change at positionforex.com? Learn about it here first!
- Links to upcoming webinars
- Attend free webinars to improve your trading.
- And Much More
- Tools, Membership-only Videos, and more will be released in the Forex Forecast.
The best part – it’s completely free.

Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Stochastic Indicator, and How Does It Work?
The Stochastic Indicator is a momentum oscillator used in Forex trading to identify overbought and oversold conditions in the market.
It compares the current closing price to a range of prices over a specified period, providing insights into the relative strength of price movements.
The indicator consists of two lines, %K and %D, which help traders gauge momentum shifts and potential price reversals.
How Do I Interpret Overbought and Oversold Conditions Indicated by the Stochastic Indicator?
When the Stochastic Indicator’s readings exceed 80%, it suggests overbought conditions, indicating that buying pressure may have reached unsustainable levels.
Conversely, readings below 20% indicate oversold conditions, signaling potential buying opportunities as prices may rebound.
Traders often use these levels to identify potential entry or exit points in the market.
What Are Signal Line Crosses, and How Can I Use Them in Trading?
Signal line crosses occur when the %K line crosses the %D line on the Stochastic Indicator.
When the %K line crosses above the %D line, it generates a bullish signal, indicating potential upward momentum and increasing buying pressure.
A bearish signal occurs when the %K line crosses below the %D line, signaling rising selling pressure and potential downward movement.
Utilize these crosses to confirm trends and identify potential entry or exit points.
How Can I Integrate the Stochastic Indicator with Other Tools and Indicators?
Integrating the Stochastic Indicator with other tools and indicators enhances its effectiveness in Forex trading.
Combine Stochastic analysis with trend analysis, Japanese candlestick patterns, chart patterns, and support/resistance levels to validate signals and improve the accuracy of trade setups.
Aligning Stochastic signals with the prevailing market conditions and confirming them with complementary techniques can enhance trading performance and profitability.
What Risks Are Associated with Relying Solely on the Stochastic Indicator for Trading Decisions?
While the Stochastic Indicator is a valuable tool for identifying potential market entry and exit points, its limitations must be acknowledged.
Relying solely on the Stochastic Indicator without considering other factors such as market fundamentals, economic indicators, and geopolitical events may result in suboptimal trading decisions.
Traders should use the Stochastic Indicator in conjunction with other forms of analysis and exercise prudent risk management to mitigate potential losses and achieve consistent profitability.