The Parabolic Stop and Reverse (PSAR) indicator is a valuable momentum indicator popular with many Forex traders.
Developed by Welles Wilder, the signal places dots above or below price bars to designate potential trend reversals.
This article will explore the indicator’s mechanics and integration with other technical analysis tools, such as the LSMA trend indicator, Japanese candlestick patterns, chart patterns, and support and resistance levels.
This exploration aims to provide you with practical insights to enhance your Forex trading strategies.
What is the PSAR Indicator?
Among the many tools available, the Parabolic Stop and Reverse is noteworthy for its ability to identify potential changes in price momentum.
Developed by Welles Wilder, the indicator employs a unique algorithm to plot dots on a price chart, serving as dynamic markers of trend direction and potential reversal points.
At its core, it operates on trailing stops.
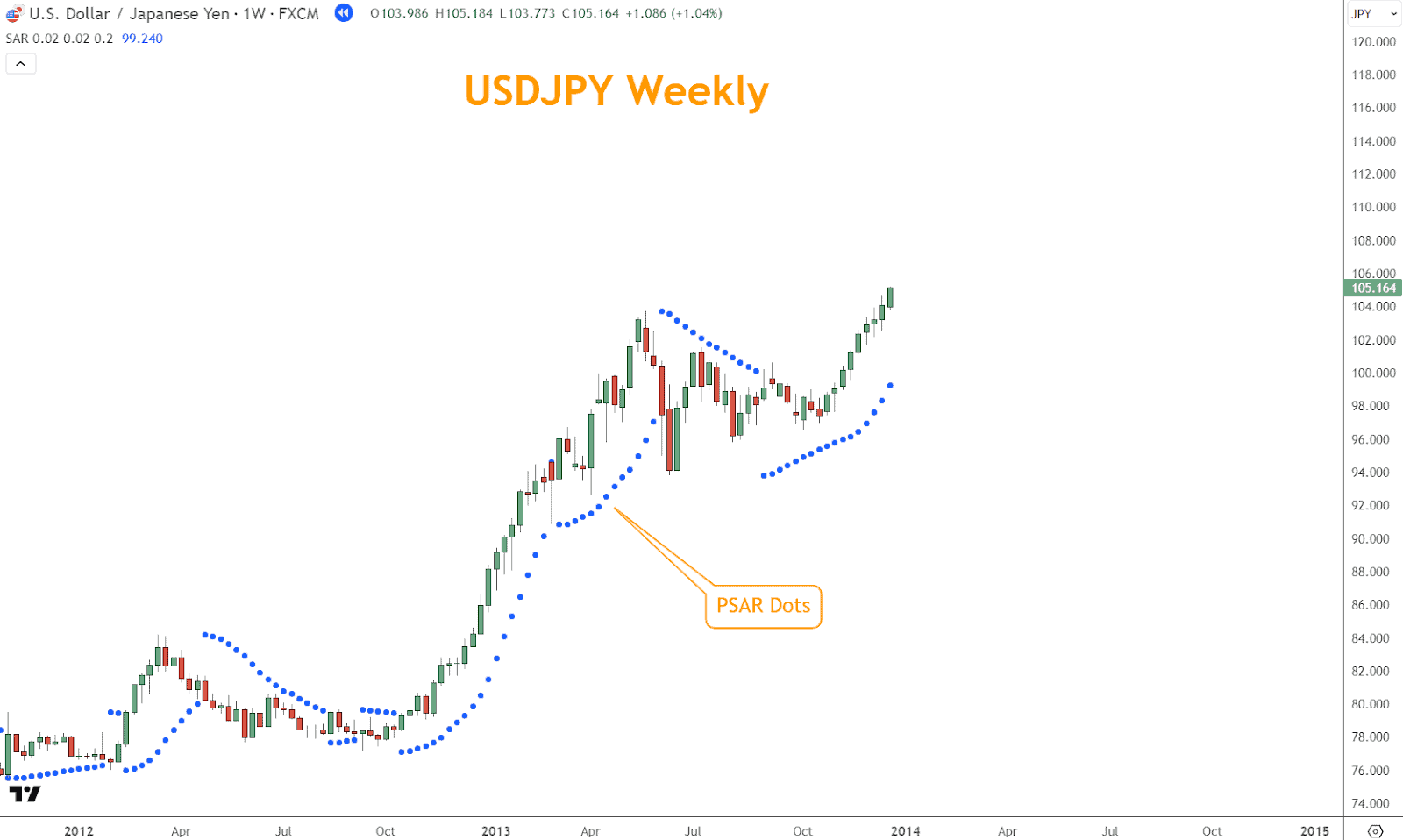
When the price rallies, the dots appear below the price bars, suggesting potential support levels and indicating bullish momentum.
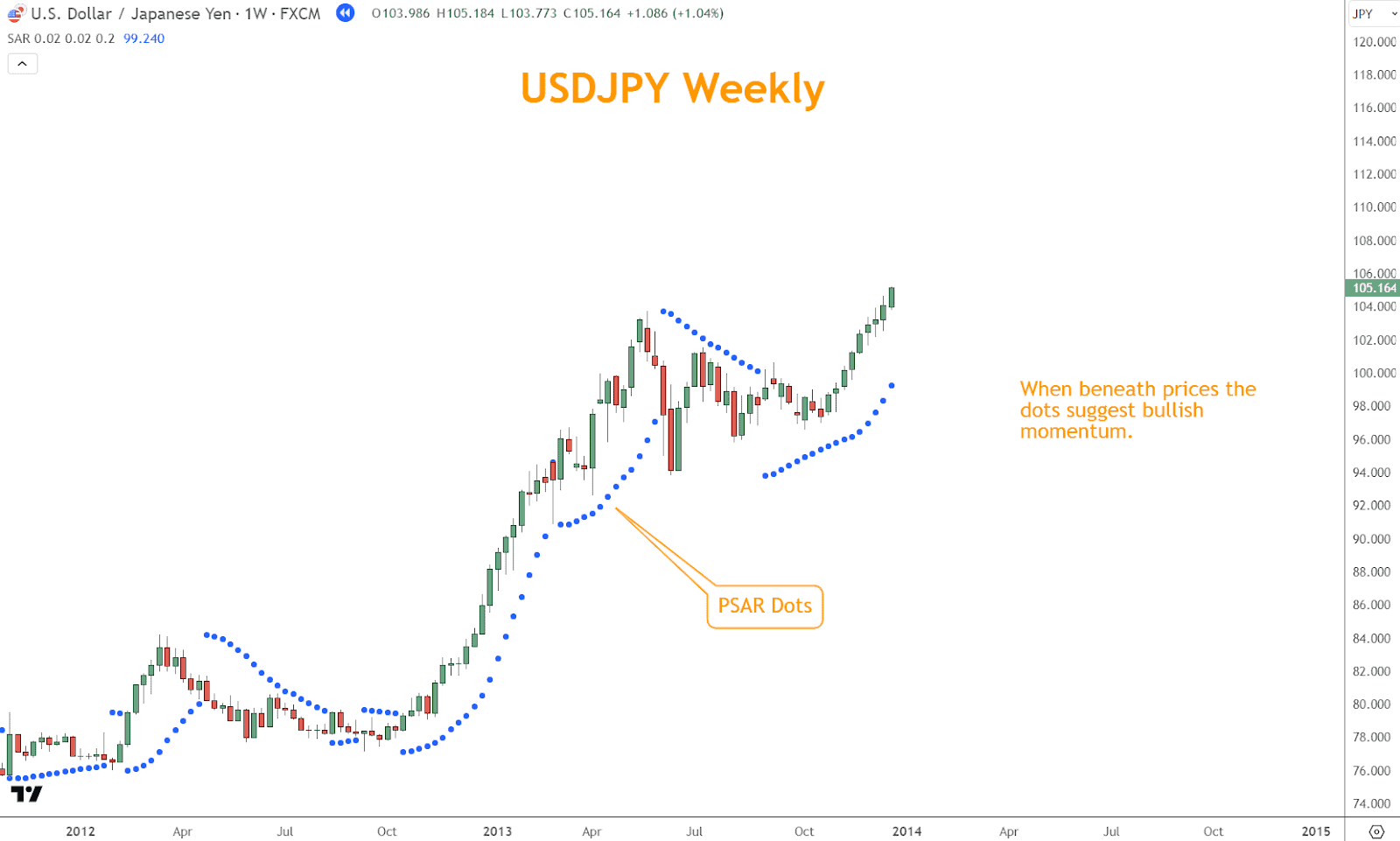
Conversely, the dots manifest above the price bars in a downtrend, delineating potential resistance levels and signaling bearish momentum.
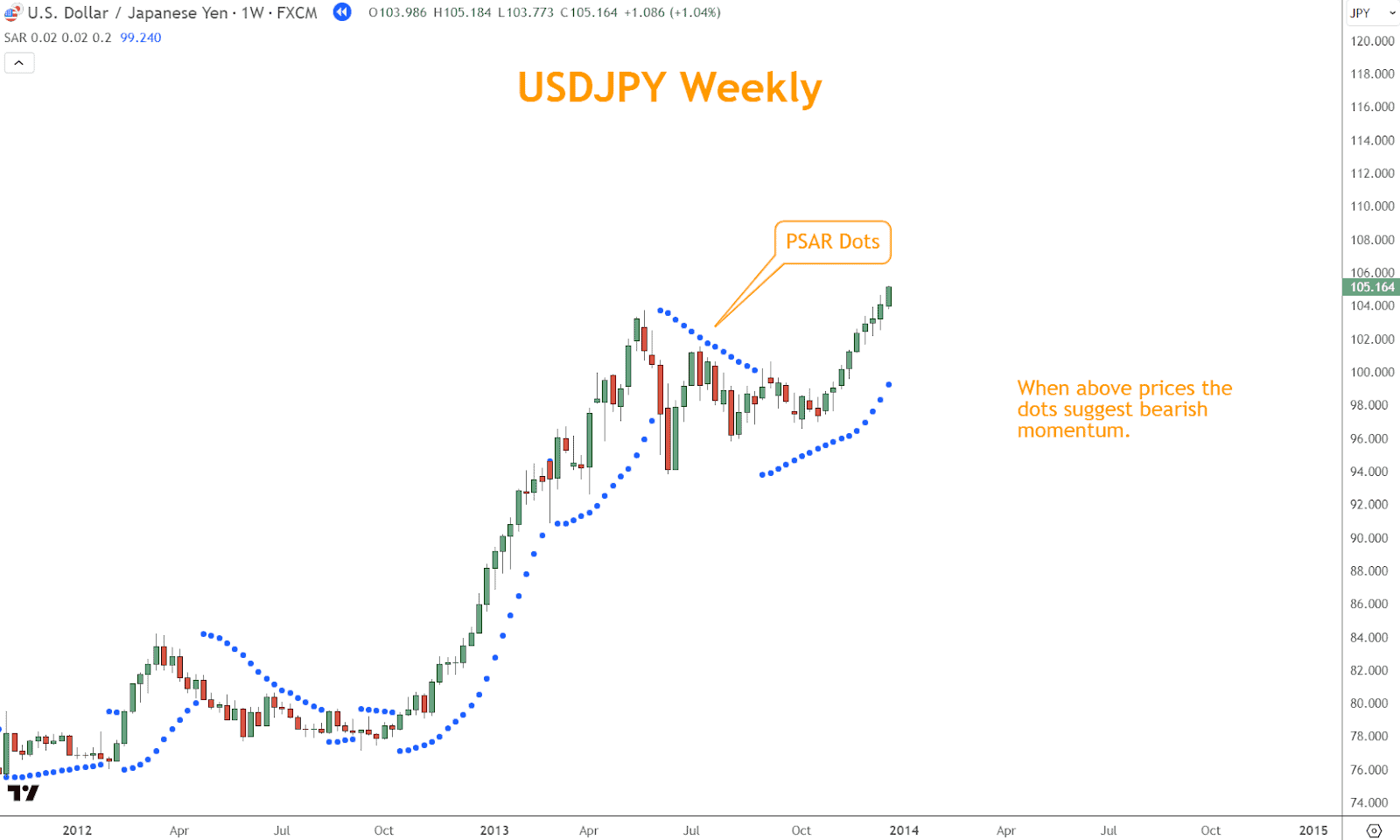
The spacing between these dots and price bars dynamically adjusts based on market volatility, offering insights into the strength and sustainability of prevailing trends.
You can leverage the indicator to identify suitable entry and exit points.
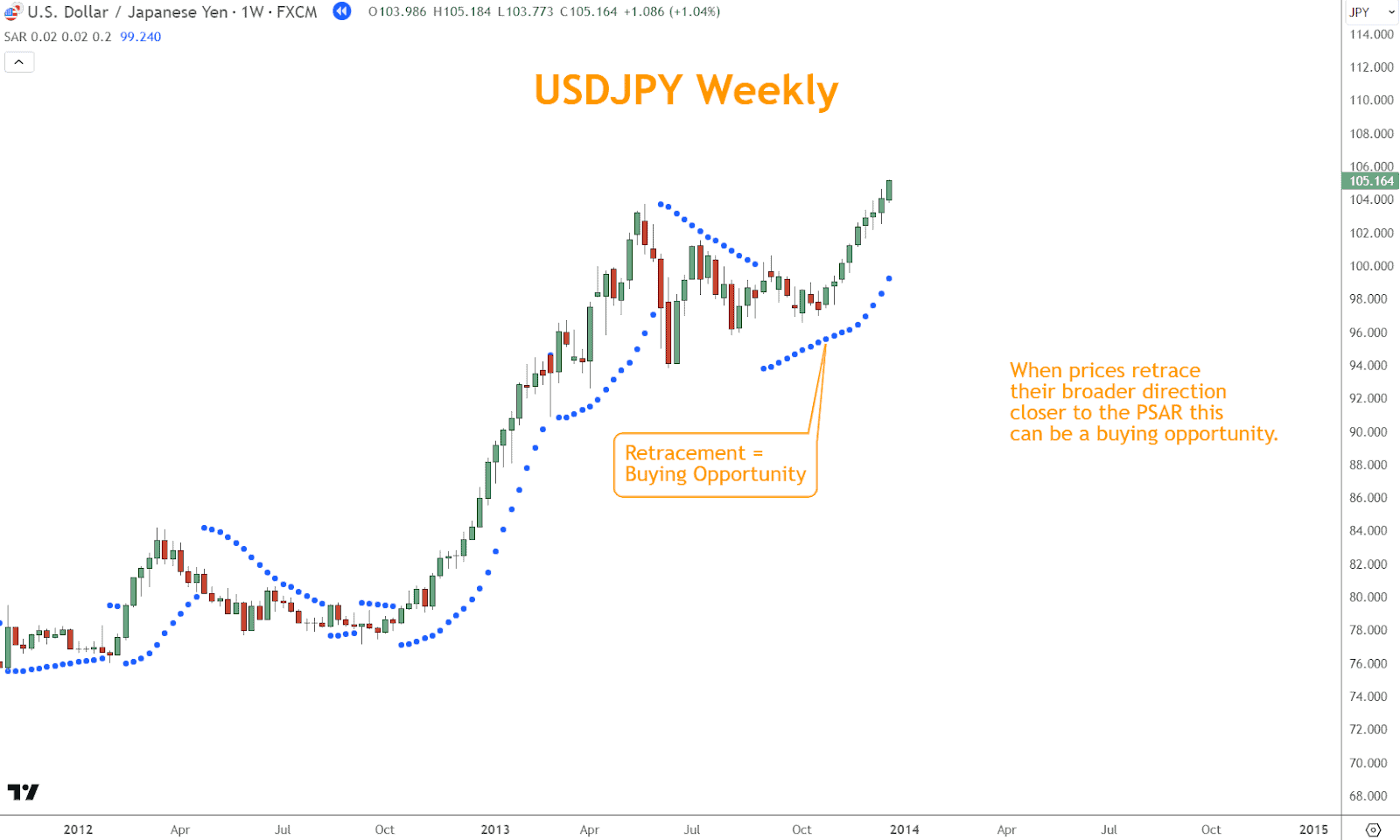
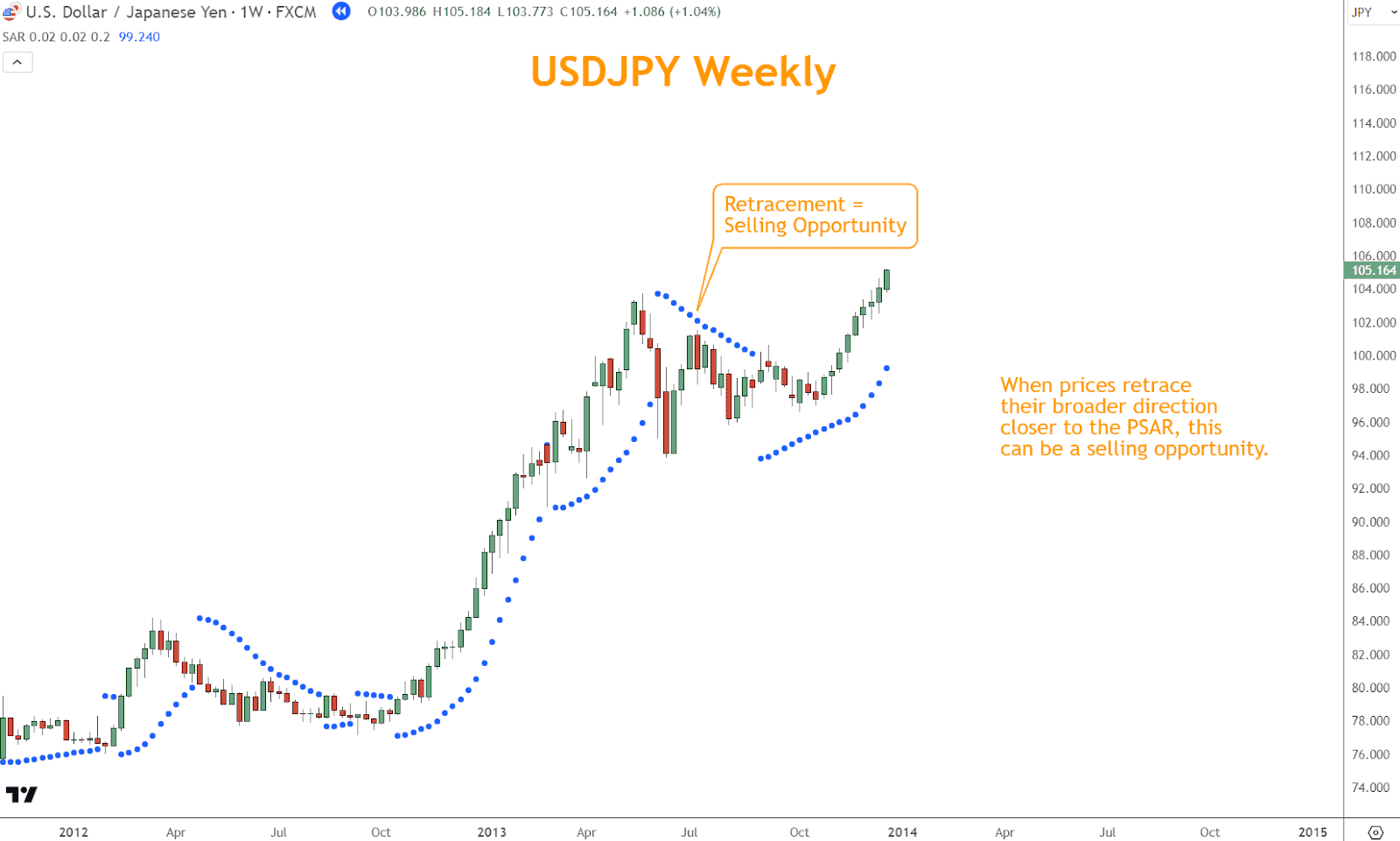
In a rally, buying opportunities may arise when the price retraces to the vicinity of the dots, signaling potential support and presenting favorable risk-reward ratios.
In the October 2013 example below, USDJPY retraced from the peak in May closer to the PSAR, which is already Bullish.
This circumstance is an excellent example of using a retracement and the PSAR together to find a quality entry.
Conversely, selling opportunities may materialize in a selloff as the price approaches the dots from below, indicating potential resistance and optimal points for initiating short positions.
After the May 2013 selloff, USDJPY retraced close to the dots before plunging lower.
This strategy is an excellent example of a bearish entry you can capitalize on using the PSAR.
Additionally, it’s a valuable tool for managing trade positions.
As the price continues its upward ascent, you may adjust your stop-losses to follow the rising dots, securing profits while allowing room for further potential upside.
Similarly, trailing stop-loss orders behind the descending dots in a selloff can help mitigate downside risk while maximizing gains as the price continues its downward trajectory.
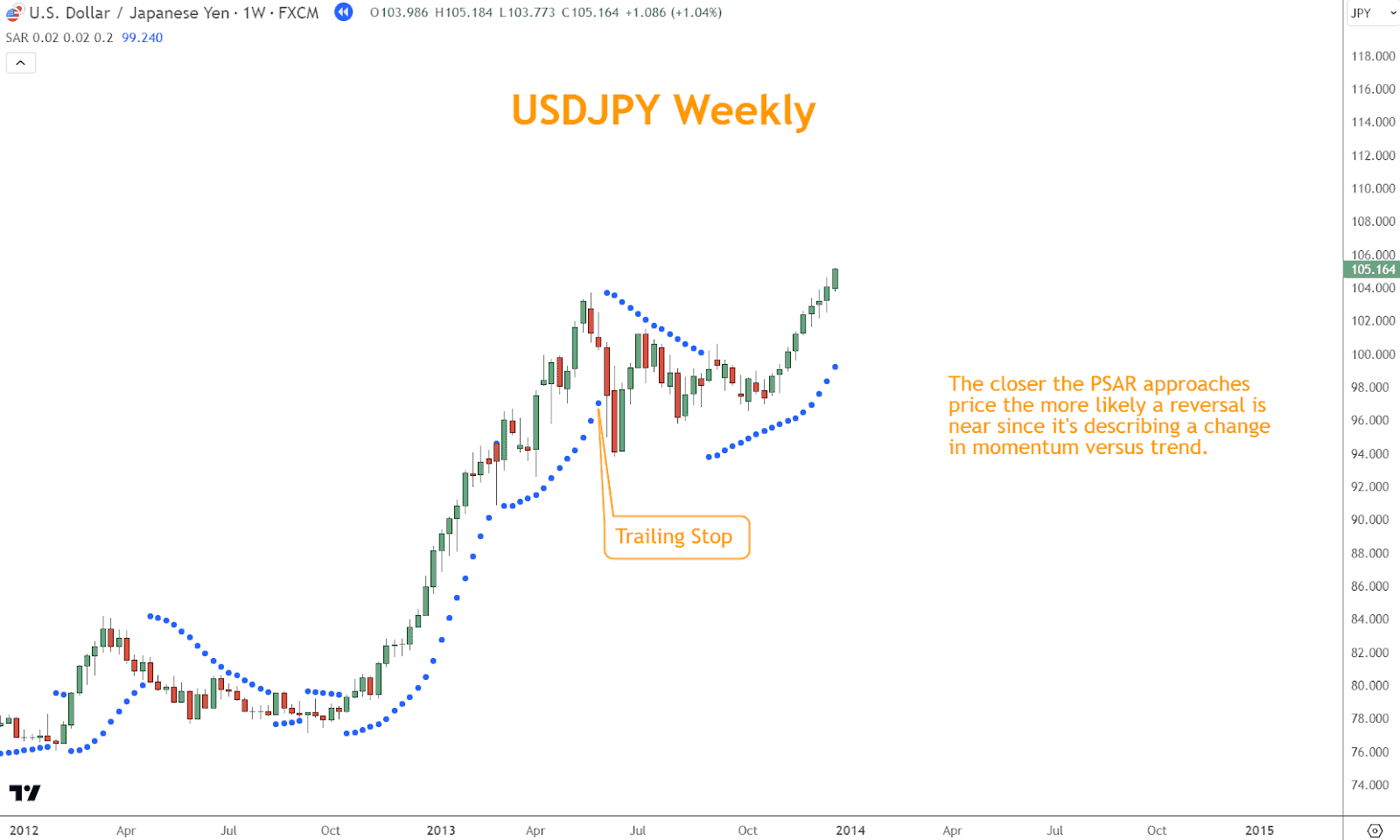
Furthermore, the PSAR can provide early warnings of potential reversals.
When the price action accelerates sharply, causing the dots to flip from one side of the price bars to another, it signifies an impending reversal in momentum.
However, the PSAR is not foolproof and should be used with other analytical tools and prudent risk management strategies.
How to Combine the PSAR with LSMA Trend Indicator
Precision and clarity are paramount in integrating multiple technical indicators into market dynamics, enhancing traders’ ability to make informed decisions.
One powerful combination that traders often employ is integrating the Parabolic Stop and Reverse with the Least Squares Moving Average (LSMA)stop-and-reverse.
Understanding the LSMA Trend Indicator
Let’s start by understanding the LSMA trend indicator before we explore how it works in tandem with PSAR.
Unlike traditional moving averages, which assign equal weight to all data points, the LSMA employs a sophisticated algorithm to provide a smoothed representation of price movements.
By minimizing the impact of outliers and noise, LSMA offers traders a clearer view of the prevailing trend direction.
The LSMA indicator calculates the linear regression line over a specified period, providing a more accurate depiction of the underlying direction.
Use the slope of the LSMA line to ascertain direction.
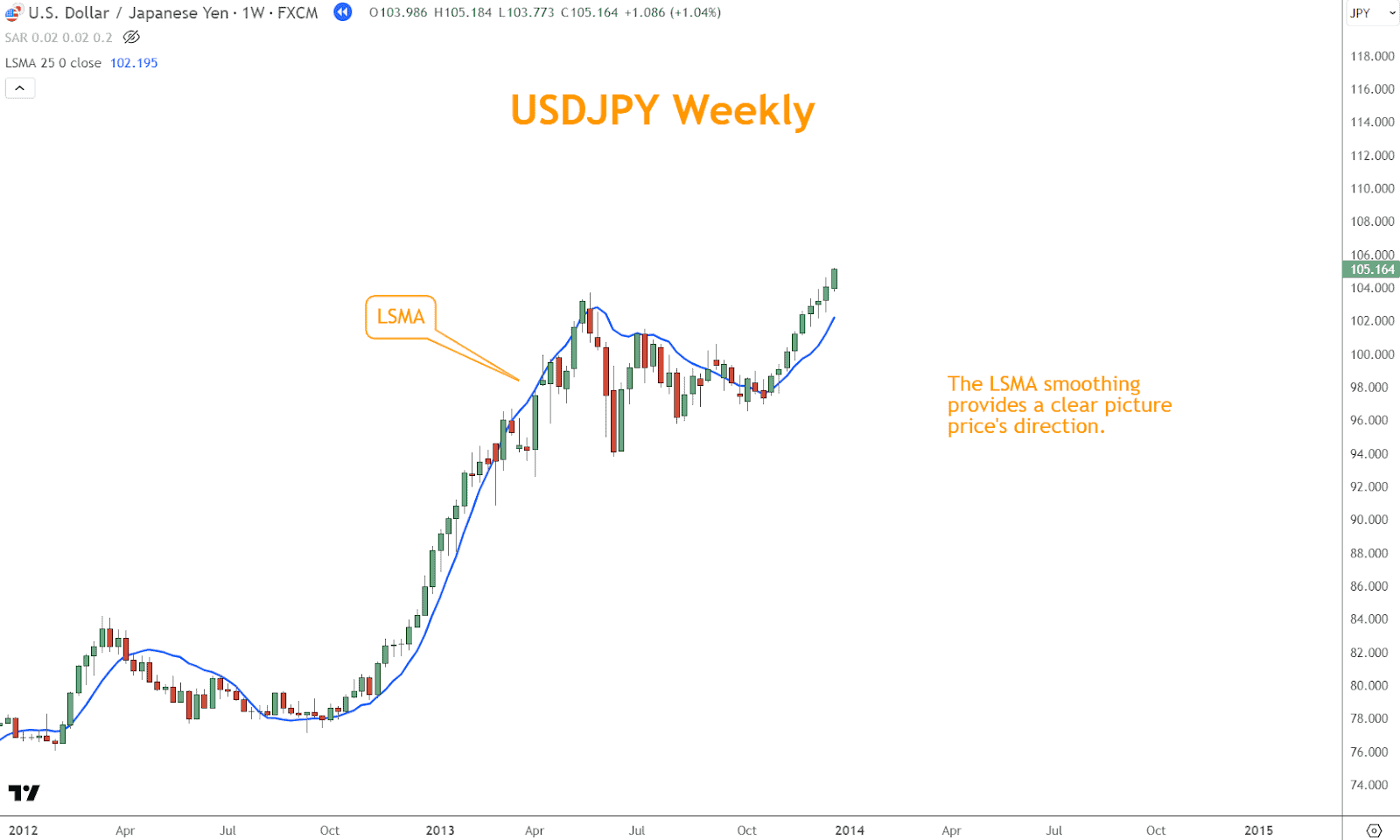
An upward slope indicates an uptrend, while a downward slope suggests a downtrend.
By aligning their trades with the predominant trend direction, you increase the probability of success and mitigate the risk of trading against the prevailing market sentiment.
Synergy between PSAR and LSMA
The PSAR and LSMA indicators offer a robust framework for analyzing market trends and identifying high-probability trade setups.
To effectively leverage this combination, look for alignment between the dots and the direction of the LSMA trend.
When the dots manifest below price bars in an uptrend confirmed by the upward slope of LSMA, it signals a potential buying opportunity.
This alignment indicates that bullish momentum is intact, with the dots serving as dynamic support levels to guide entry points.
Conversely, when the dots appear above price bars amidst a selloff indicated by the downward slope of LSMA, it suggests a selling opportunity.
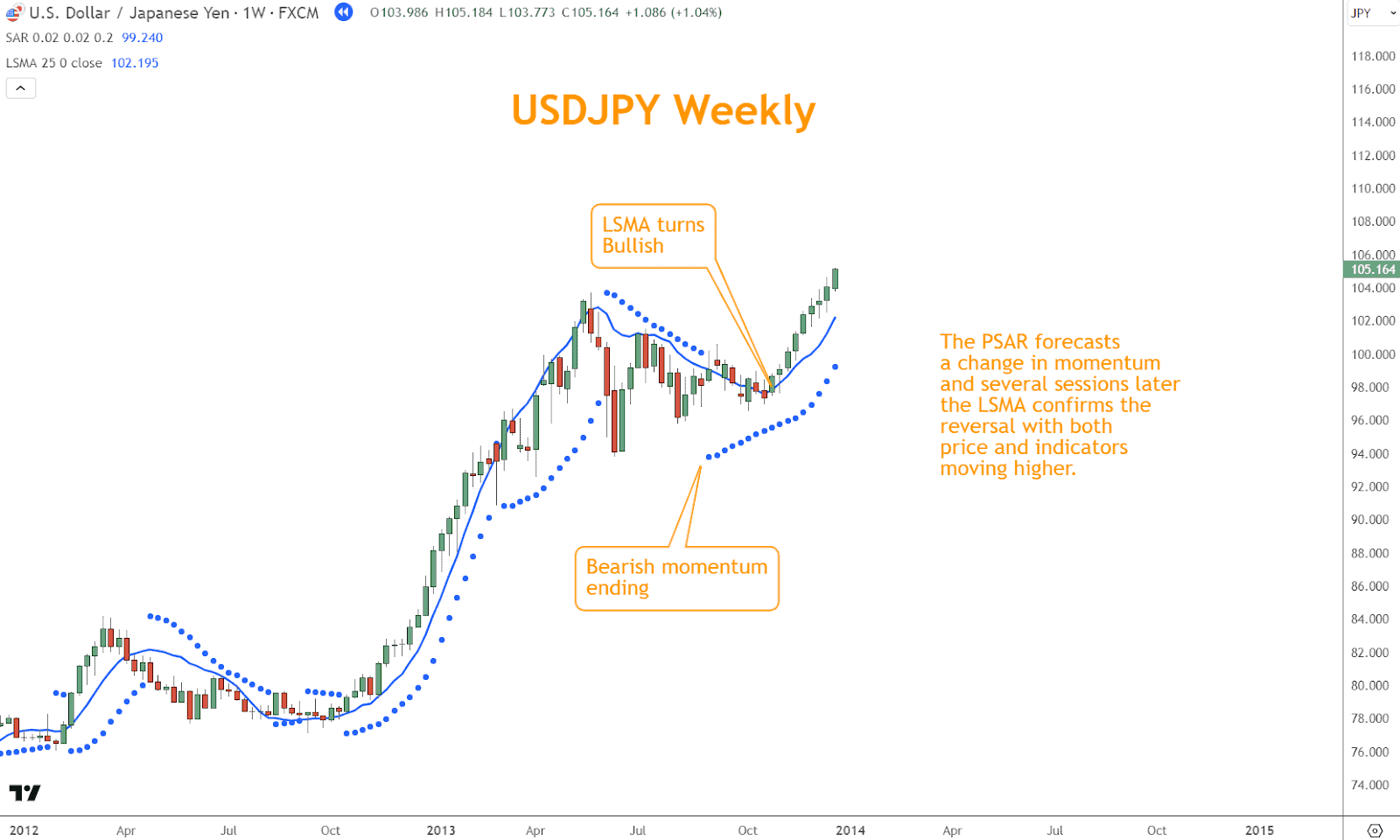
In the example above, the PSAR forecasts a change in momentum, and several sessions later, the LSMA confirms the reversal, with both price and indicators moving higher.
By synchronizing their trading decisions with the convergence of PSAR and LSMA signals, you can enhance the accuracy of your entries and exits.
How Can Japanese Candlestick Patterns be Integrated?
Japanese candlestick patterns offer profound insights into market sentiment and price action, providing valuable signals for decision-making.
When integrated with the Parabolic Stop and Reverse, Japanese candlestick patterns can enhance the precision and effectiveness of trading strategies.
Understanding Japanese Candlestick Patterns
Japanese candlestick patterns originated centuries ago in the rice markets of Japan and have since become a staple tool for traders worldwide.
Each candlestick represents a specific time frame encapsulating four key price points: the opening price, closing price, highest price (high), and lowest price (low).
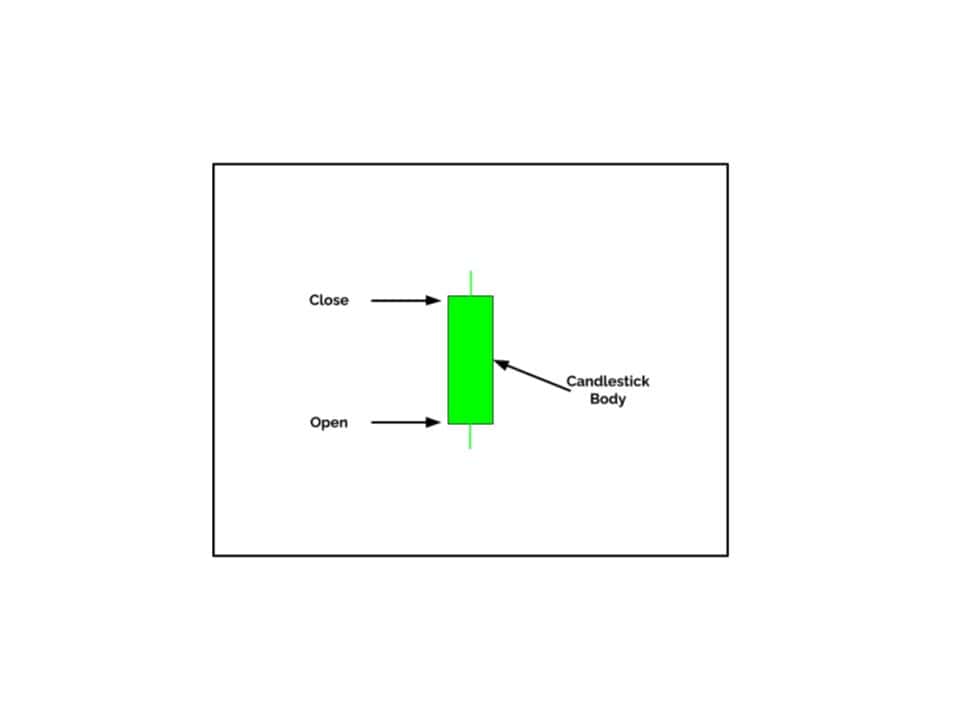
Candlestick patterns are categorized into bullish and bearish formations, conveying distinct messages about market dynamics.
Bullish patterns like Hammer, Engulfing, and Morning Star signal upward reversals.
Conversely, bearish patterns, including the Shooting Star, Engulfing Pattern, and Evening Star, indicate potential reversals to selloffs.
Integration with PSAR Indicator
Combining the indicator with Japanese candlestick patterns offers a comprehensive framework for analyzing market dynamics and identifying high-probability trade setups.
You can leverage these patterns to validate signals, enhancing their accuracy in trading decisions.
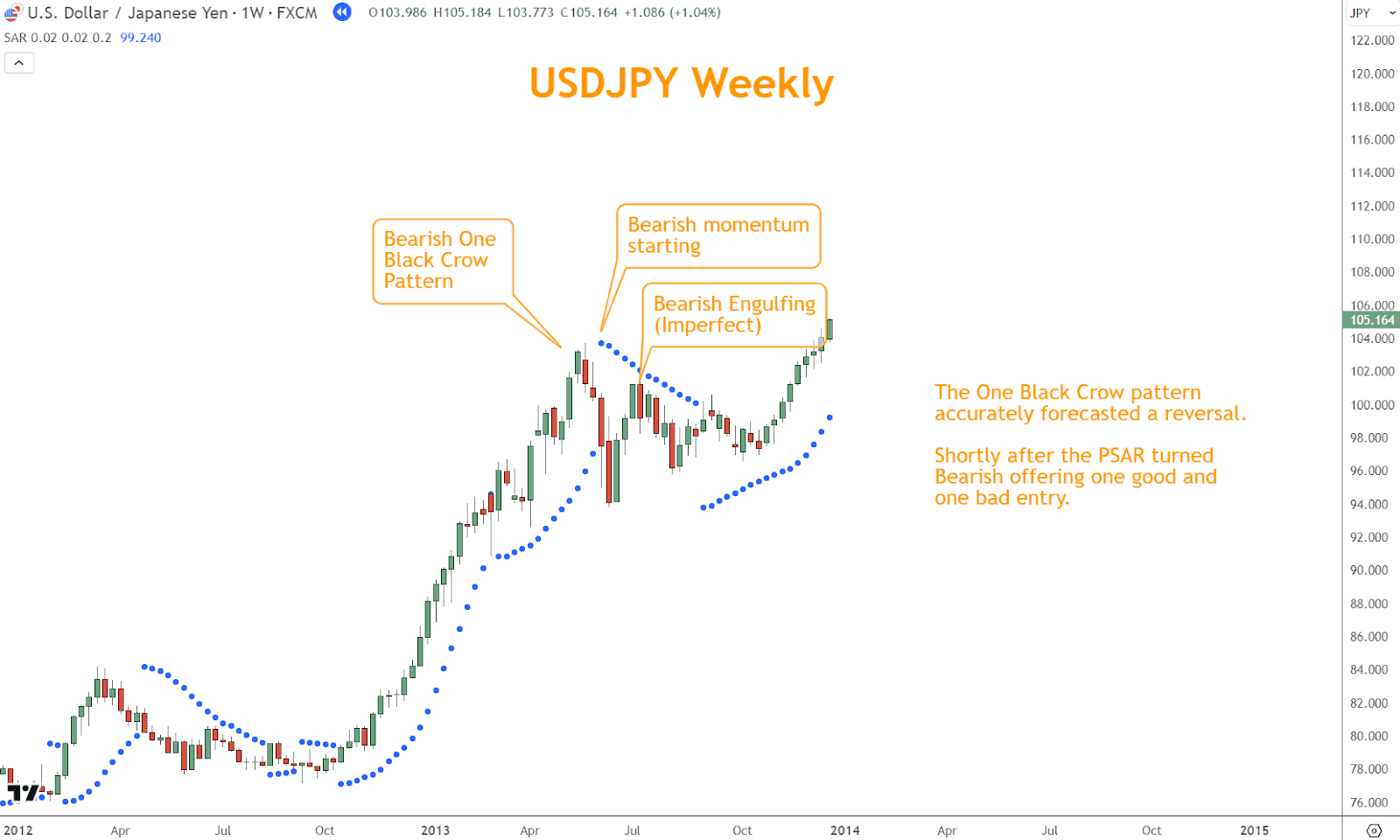
The One Black Crow pattern accurately forecasted a reversal, as shown in the example below.
Shortly after, the PSAR turned Bearish, offering one good and one poor entry.
The first entry lasted only one candle and then reversed. The second entry, USDJPY, was much closer to the dots and gave a better entry and more manageable stop.
Can You Utilize Chart Patterns Too?
Chart patterns offer valuable insights into potential price movements and reversals.
Recognizing and understanding these patterns can help you make more informed decisions about when to enter or exit trades.
When integrated with the Parabolic Stop and Reverse, chart patterns become even more powerful, providing traders with comprehensive signals for navigating the complexities of the Forex market.
Understanding Chart Patterns
Chart patterns represent price movements that repeat over time, indicating potential continuations or reversals.
Continuation patterns suggest that the prevailing direction is likely to persist, while reversal patterns indicate a potential change in direction.
Common continuation patterns include Flags, Pennants, and Triangles.
Below is an example of commonly used Triangle patterns.
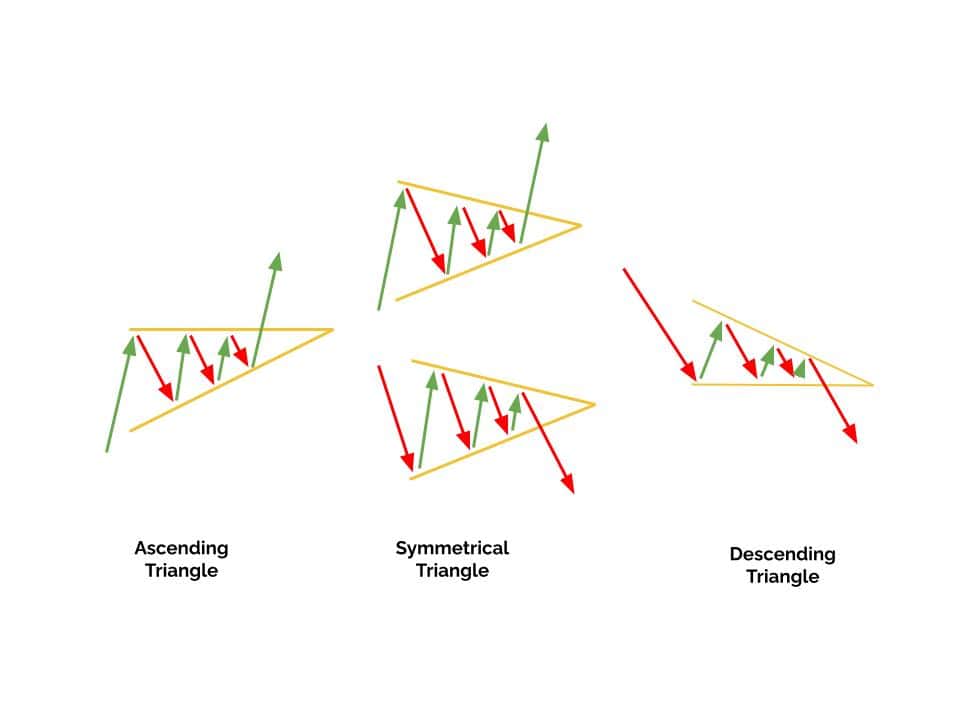
These patterns typically occur during an existing rally or selloff and suggest a temporary pause before resuming.
Reversal patterns, such as Head and Shoulders, Double Tops, and Double Bottoms, signal a potential reversal of the prevailing direction and often mark significant turning points in price action.
Integration with PSAR Indicator
Combining chart patterns with the indicator offers traders a comprehensive framework for analyzing market dynamics and identifying high-probability trade setups.
You can use chart patterns to validate signals generated, enhancing their trading strategies’ accuracy and reliability.
For instance, let’s consider a scenario where the indicator signals a potential bullish reversal, with dots appearing below price bars, indicating a shift in momentum.
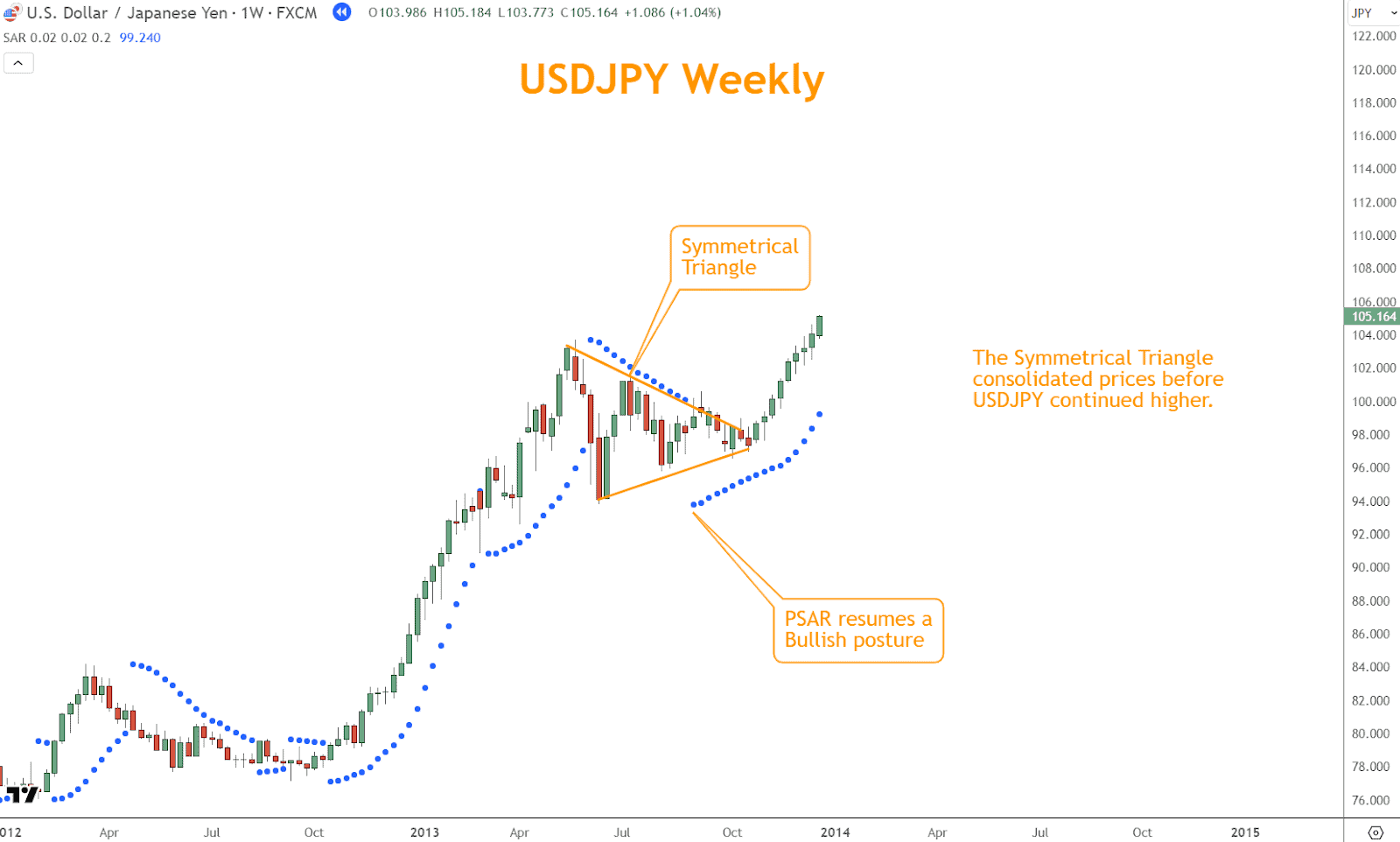
In the example above, the Symmetrical Triangle consolidated prices before USDJPY continued higher.
The triangle’s apex and the coinciding bullish PSAR signal provide an excellent long entry on USDJPY.
Can Support and Resistance Levels Combine with the PSAR Indicator?
Support and Resistance levels are fundamental concepts in technical analysis.
They serve as critical reference points where buying and selling pressure converge.
These levels are crucial in identifying potential trade entry and exit points and understanding the broader market dynamics.
When integrated with the Parabolic Stop and Reverse, support and resistance levels provide invaluable insights into market behavior and help validate trading signals.
Understanding Support and Resistance Levels
Support levels are price levels where buying interest is sufficiently strong to prevent the price from falling further.
These levels often correspond to previous lows in price action.
Floors can be arranged diagonally or horizontally in channels that support the market.
On the other hand, Resistance levels are price levels where selling pressure outweighs buying pressure, preventing the price from rising further.
Resistance levels typically coincide with previous highs in price action and act as ceilings that cap the market’s upward movement.
You can use Support and Resistance levels to identify potential reversal points and determine optimal entry and exit points for trades.
When the price approaches a Support or Resistance level, observe how the market reacts at these levels to anticipate future price movements.
Integration with the PSAR Indicator
Support and Resistance levels offer additional confirmation for trading signals and refine your entry and exit strategies.
Use these levels to validate signals, increasing your trading decisions’ reliability.
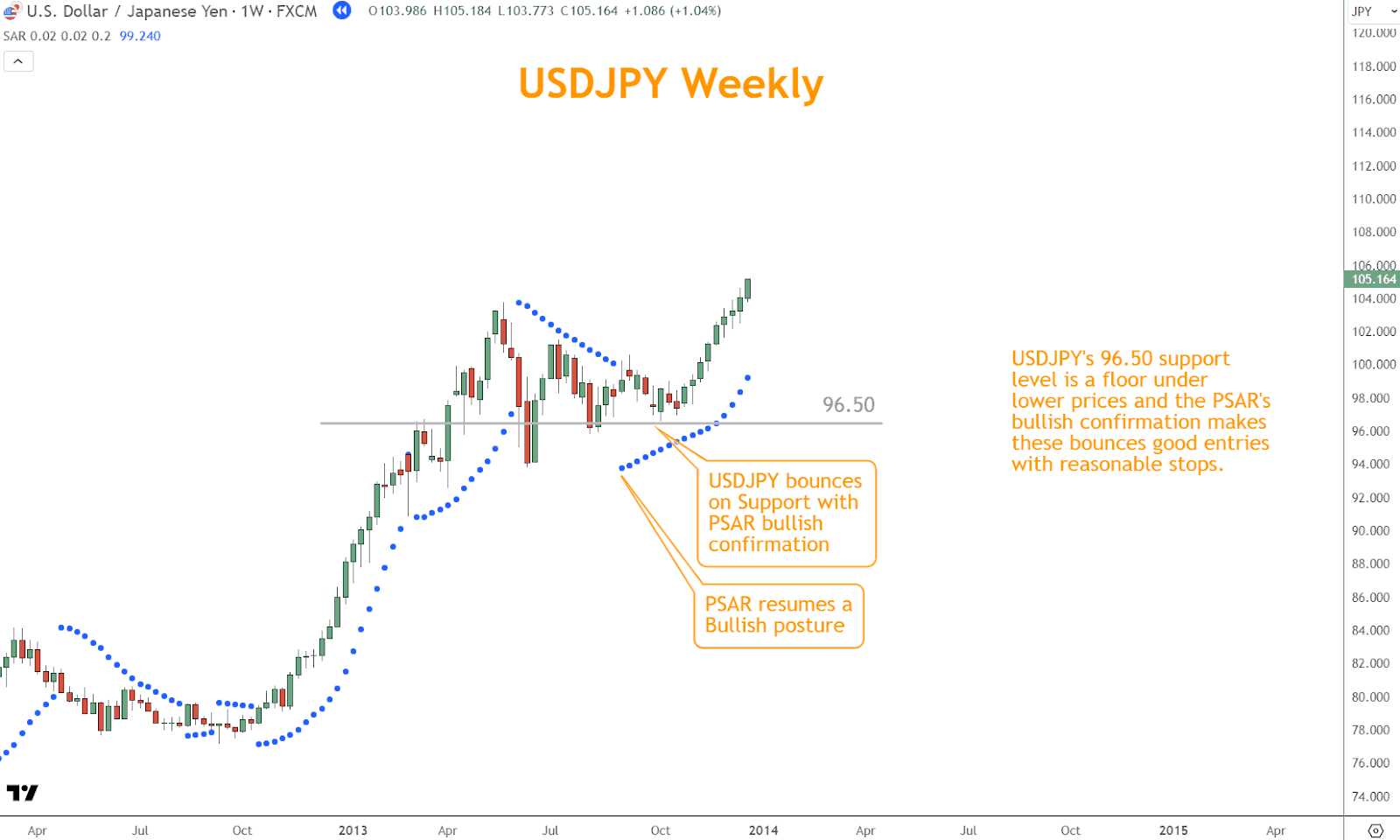
In the example above, USDJPY’s 96.50 support level is a floor under lower prices, and the PSAR’s bullish confirmation makes these bounces attractive entries with a reasonable stop.
Together, these techniques provide an entry and exit solution when price action near support or resistance coincides with the PSAR’s signal.
What’s the Next Step?
Consider your trading strategy and how the PSAR could help your trading.
In addition, look for opportunities to use what you’ve learned and incorporate it into your trading habits.
If you need help developing an analysis process, you can use our Six Basics of Chart Analysis. If you’re unfamiliar with the Six Basics, you can learn them here for free.
The “Six Basics” will give you a strong foundation in chart analysis, which you can incorporate into your knowledge of the PSAR.
In addition, when you get the “Six Basics,” you’ll also get Forex Forecast delivered to your inbox every Sunday.
Forex Forecast includes:
- Trade Ideas and Analysis
- I will use the Six Basics of Chart Analysis and Advanced Strategies to show you the trade opportunities I’m watching.
- Case Studies from Around the Web
- Watch how applying the Six Basics worked on some of the best, most profitable trades.
- Trading Education Guides and Videos
- Want to learn most Six Basics techniques and advanced strategies?
- I produce videos and guides to help you learn and improve trading practices.
- Links to New Articles
- I publish new articles on topics traders will want to know about every week, and you can find out when they post.
- Positionforex.com News
- Did something change at positionforex.com? Learn about it here first!
- Links to upcoming webinars
- Attend free webinars to improve your trading.
- And Much More
- Tools, Membership-only Videos, and more will be released in the Forex Forecast.
The best part – it’s completely free.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Parabolic Stop and Reverse and why is it Significant in Forex Trading?
The Parabolic Stop and Reverse is a technical analysis tool developed by Welles Wilder.
It is significant in Forex trading because it helps traders identify potential shifts in price momentum by placing dots above or below price bars to signal potential trend reversals.
How does the Indicator Operate, and what Insights does it Provide to Traders?
The signal operates on trailing stops, dynamically placing dots above or below price bars.
These dots offer insights into the strength and sustainability of prevailing trends and adjust based on market volatility.
Can you Explain the Synergy Between the PSAR and LSMA Trend indicators?
The two indicators can combine to confirm directions and pinpoint optimal entry and exit points.
When dots align with the direction of the LSMA trend, it signals potential buying or selling opportunities.
How do Japanese Candlestick Patterns Enhance Forex Trading Strategies when Integrated with the PSAR?
Japanese candlestick patterns offer valuable validation for PSAR signals.
For instance, bullish patterns like Hammers or Engulfing patterns near support levels validate bullish signals.
In contrast, bearish patterns like Shooting Stars or Engulfing Patterns near resistance levels validate bearish signals.
What role do Support and Resistance Levels play and how can Traders Effectively Utilize Them?
Support and Resistance levels are critical reference points where buying and selling pressure converge.
Traders can validate signals by observing price reactions at these levels, reinforcing their trading decisions.
For example, bounces off support levels during bullish signals or rejections near resistance levels during bearish signals confirm initiating trades.

