The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) indicator is a technical indicator based on moving averages used in Forex trading.
This indicator can determine trend direction, find reversals and momentum divergence, and generate trading signals on any timeframe.
The strategy can be applied to different time frames and is commonly used with indicators such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI).
This article will cover Moving Average Convergence Divergence strategies such as crossover, divergence, zero-cross, and combining MACD and RSI.
I’ve been trading Forex and other markets since 2007 and have examined the usefulness of the MACD as a trend indicator versus other indicators.
What is the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) Indicator?
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) indicator is a technical trading indicator created by Gerald Appel in the late 1970s.
It tracks trends and momentum over time and consists of three components: two exponential moving averages (EMA) and a histogram.
The MACD compares the relationship between two different EMAs (exponential moving averages).
In addition, you can use the indicator as a trend confirmation and divergence tool to generate trading signals.
The MACD uses two lines that oscillate around a zero line, called the signal line.
You can look for a crossover signal when the MACD line crosses the signal line, which indicates potential price movement in either direction.
Once a crossover signal occurs, you can consider trading based on any direction indicated by the MACD and signal lines.
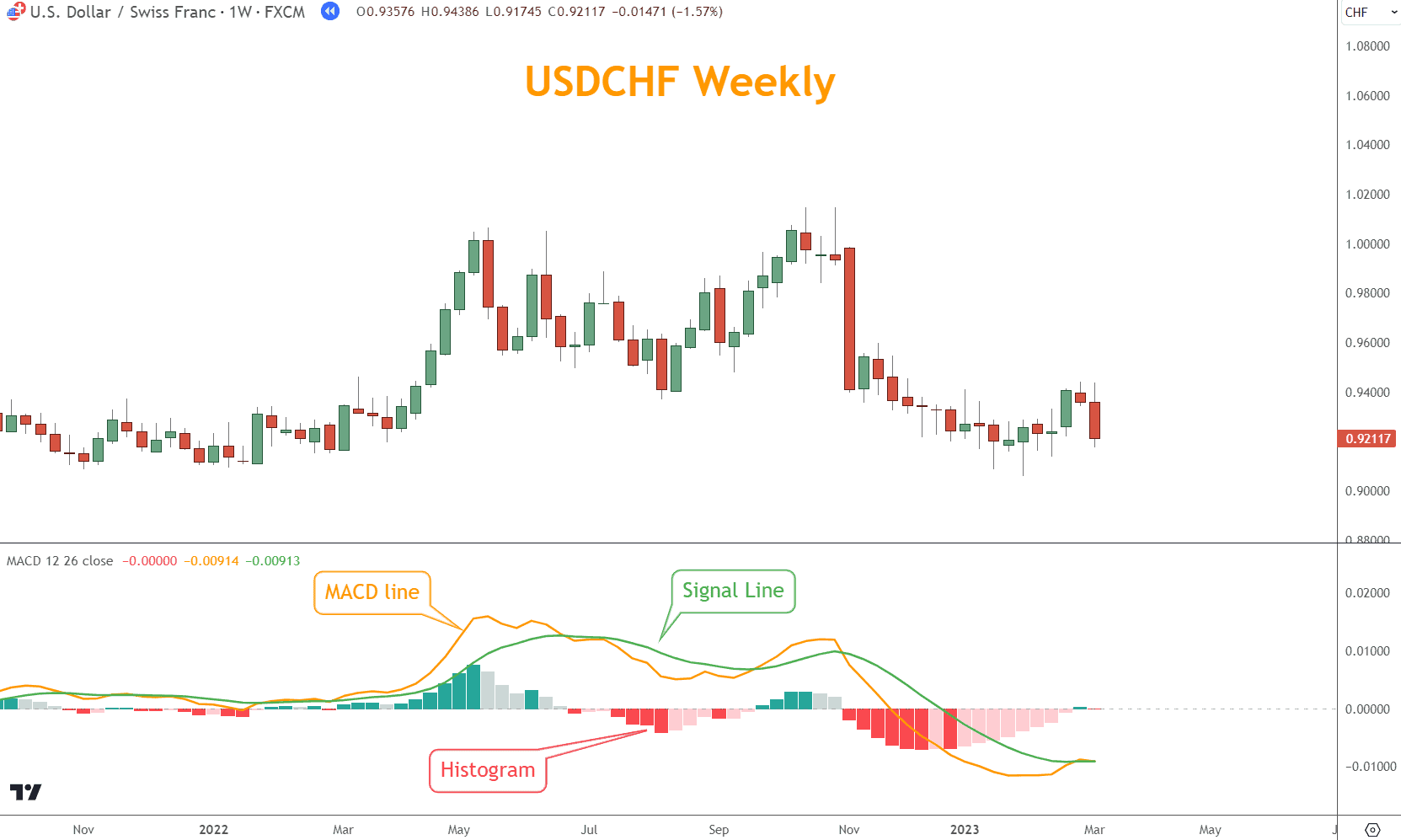
In the chart below, USDCHF moved lower in June and July 2022, and at the same time, the signal line crossed above and below the MACD line. Why?
The MACD is built with moving averages and lags price action.
Consequently, the bullish cross is a reaction to April 2022’s rally. The bearish cross comes later, but not before prices have turned and are moving higher.
If you trade exclusively with crosses, you are vulnerable to whipsawing and using late signals, which can result in losses.
Why use 12 and 26?
The default configuration parameters on most platforms are 12 and 26-period EMA. A 9-period smoothing calculation is also available.
However, you can customize these parameters to suit their trading strategy needs.
The default settings are sometimes attributed to a six-day workweek and approximately 26 working days a month.
This makes no sense since there wasn’t a six-day work or trading week in the 1970s when the MACD came to fruition.
Since the trading week is five days, traders may opt to change these parameters, but in this discussion, we’ll stick with the popular default settings.
What are the Advantages of the MACD Indicator?
The indicator remains a popular indicator because:
- It provides traders with a visual representation of an asset’s price action.
- Creates easy-to-interpret and clear signals.
- Can detect divergence between moving average signals and market price action.
What are the Disadvantages of the MACD Indicator?
- Yields false signals in markets that are trading sideways.
- DIvergence strategies produce many false signals.
- It only works best in conjunction with other technical indicators.

The Most Popular Trader Strategy: Crossover Strategy
The most popular trading strategy is the crossover strategy, which involves watching for the “fast” line to cross over or under the slower line, which signals a buy or sell signal.
However, the histogram can also signal crossovers by showing a zero figure when the two lines cross over or under each other.
In addition, the histogram shows the absolute values difference between two lines on the chart—one representing price lows and the other price highs.
Many traders use the zero line as a filter.
Even if a Bullish cross occurs, they won’t take the trade unless the MACD line exceeds the zero line.
Conversely, a Bearish cross is only considered if it happens below the zero line.
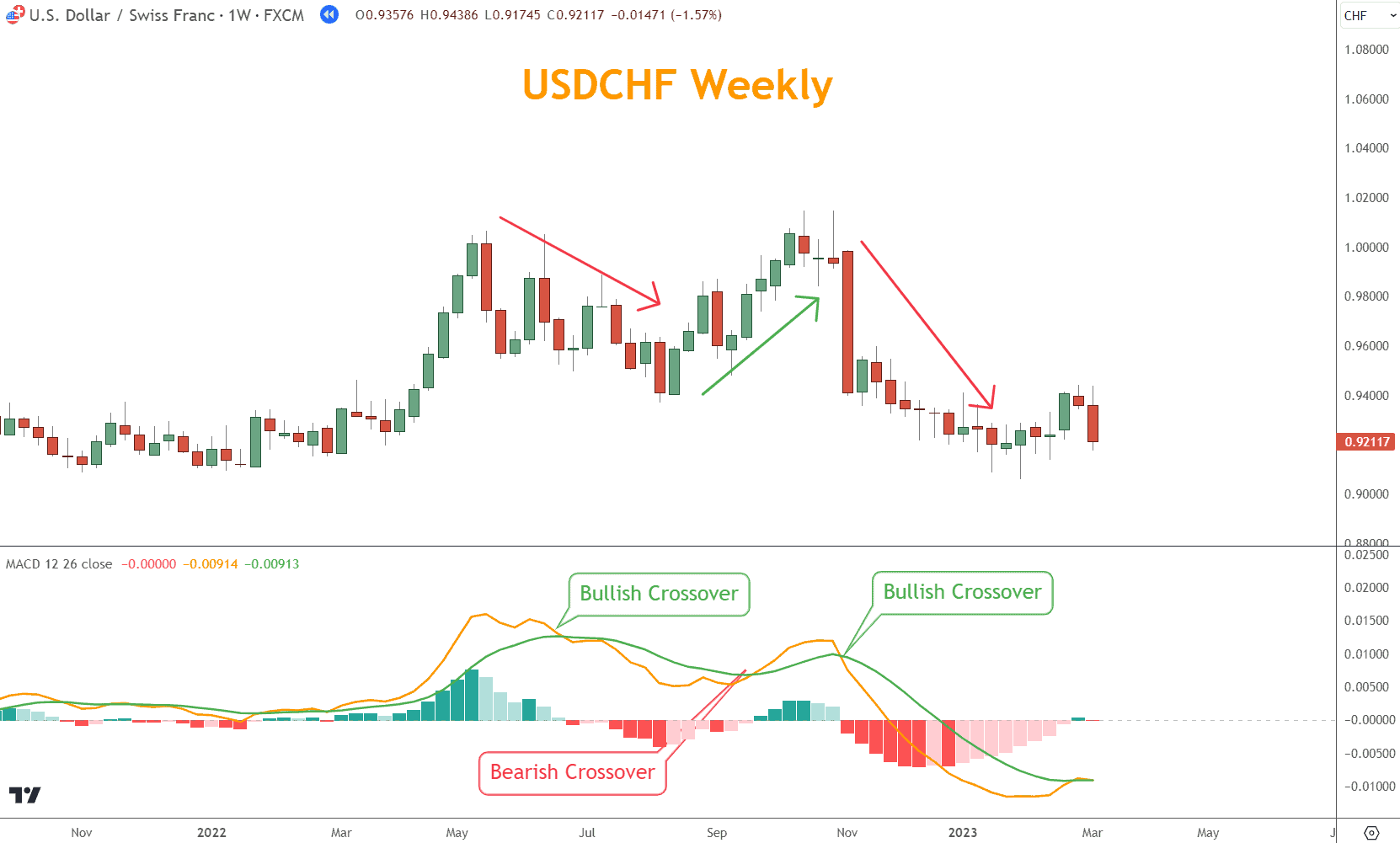
As you can see in the examples, the crossover strategy works well when prices are trending but is easily fooled in choppier and sideways markets.
This example is a sideways market, and both entry signals come too late for them to be effective.
If those signals are taken, they result in losing trades.
Does Trading Divergence Work? How?
Another strategy is divergence trading, where you can look for the MACD to move in one direction while the instrument’s price moves in another.
This strategy aims to take advantage of the MACD’s momentum component.
The logic is that if the price rises but momentum falls, a reversal is coming soon. For traders, Falling Momentum signals that the rally is weakening and foreshadows a change in direction.
Unfortunately, divergence is too often a false signal but is still one many traders like to track and consider.
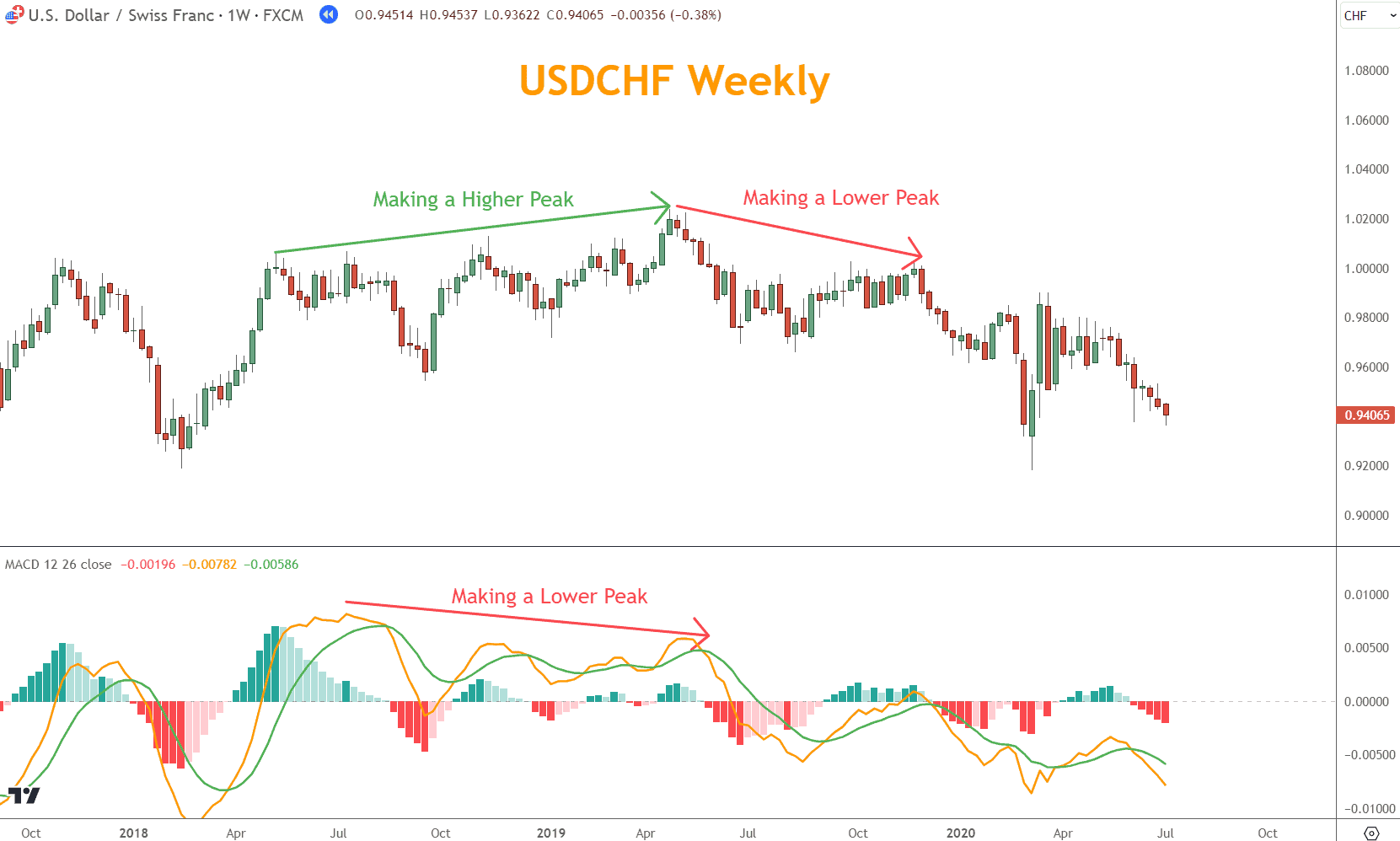
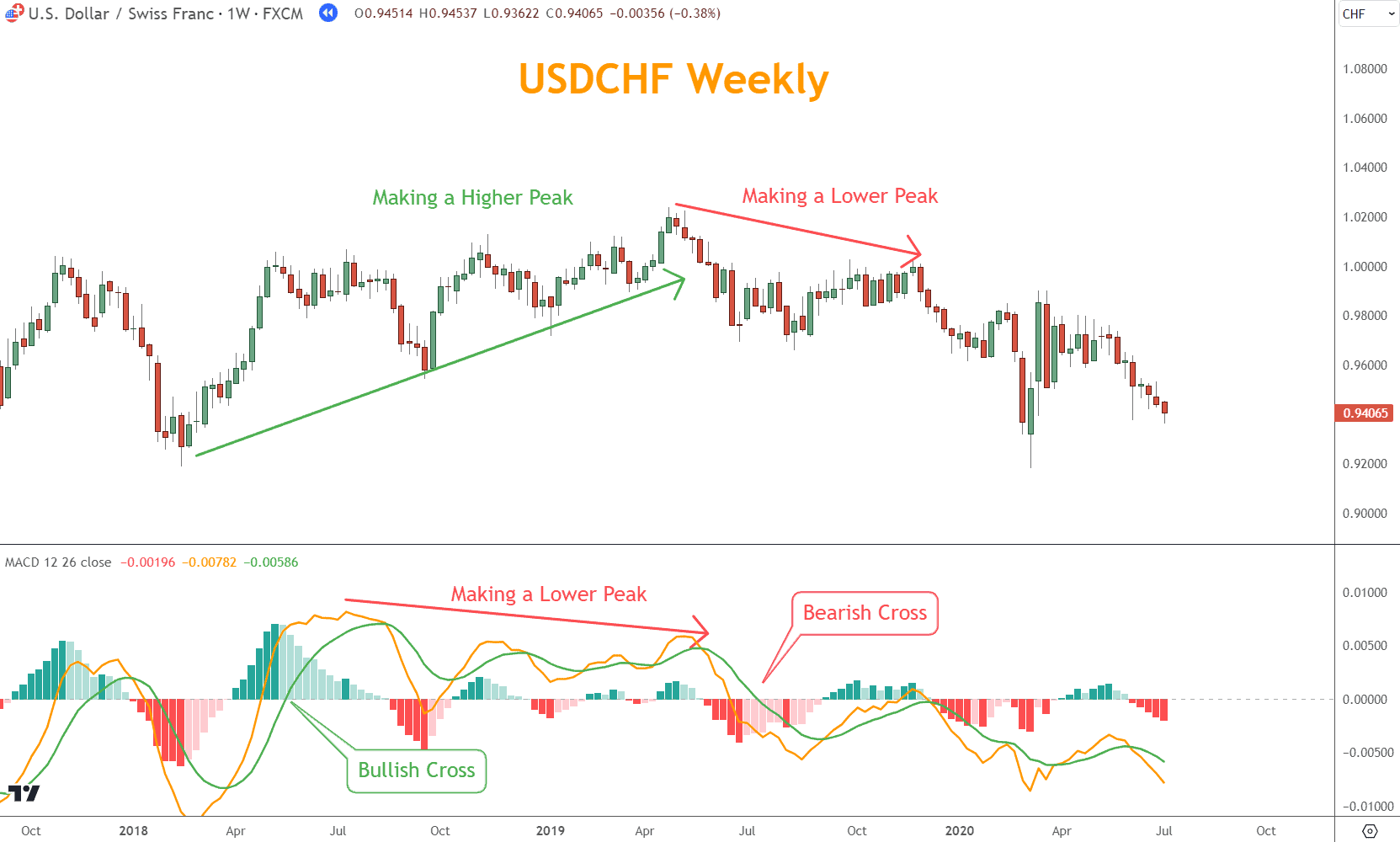
In the example below, divergence works perfectly.
USDCHF made higher highs from July 2018 to June 2019, while the MACD made a lower peak over the same period.
The result is a selloff after the lower peak.
What is the Zero-Cross Strategy Good For?
A MACD indicator is a trading protocol that generates Bullish or Bearish signals when the MACD line crosses the zero line.
The indicator plots average lines on a chart over time. When the moving average lines cross the zero line, it indicates a reversal in trend and signals you to take action.
The longer the histogram bars, the stronger the signal since the histogram tracks the difference between the MACD line and the signal line.
So, if the distance is substantial, the theory is that momentum is significant and the signal is strong.
The example below includes Bullish and Bearish crosses resulting in long and short positions.
In the example below, the MACD finally crosses the zero line, and judging by the histogram, it does so with substantial momentum.
Unfortunately, the signal is late because it lags price action and provides a poor entry.
Which Indicator Works Best With the MACD Strategy?
The RSI is among the most popular complementary indicators for trading with the MACD.
The RSI is often selected because the MACD’s greatest weakness is its lagging nature. Since it’s built around moving averages, which are lagging indicators, entry and exit timing lags, too.
Lagging indicators often signal too late for entries and exits, hurting trades. The RSI is considered a superior momentum indicator and works better when combined.
Therefore, this strategy uses the MACD only as a trend indicator, and the RSI is used for momentum.
Examine This Combination in a Forex Example
The MACD indicator can be used in Forex trading to determine an instrument’s trend, and the RSI is an oscillator that measures a particular market’s momentum.
The RSI’s “zero line” is 50; an instrument is oversold when the RSI is below 30 and overbought above 70.
Using the crossover strategy and looking for the RSI to move from overbought or oversold extremes across its “50 line” should provide valid signals.
Let’s see.
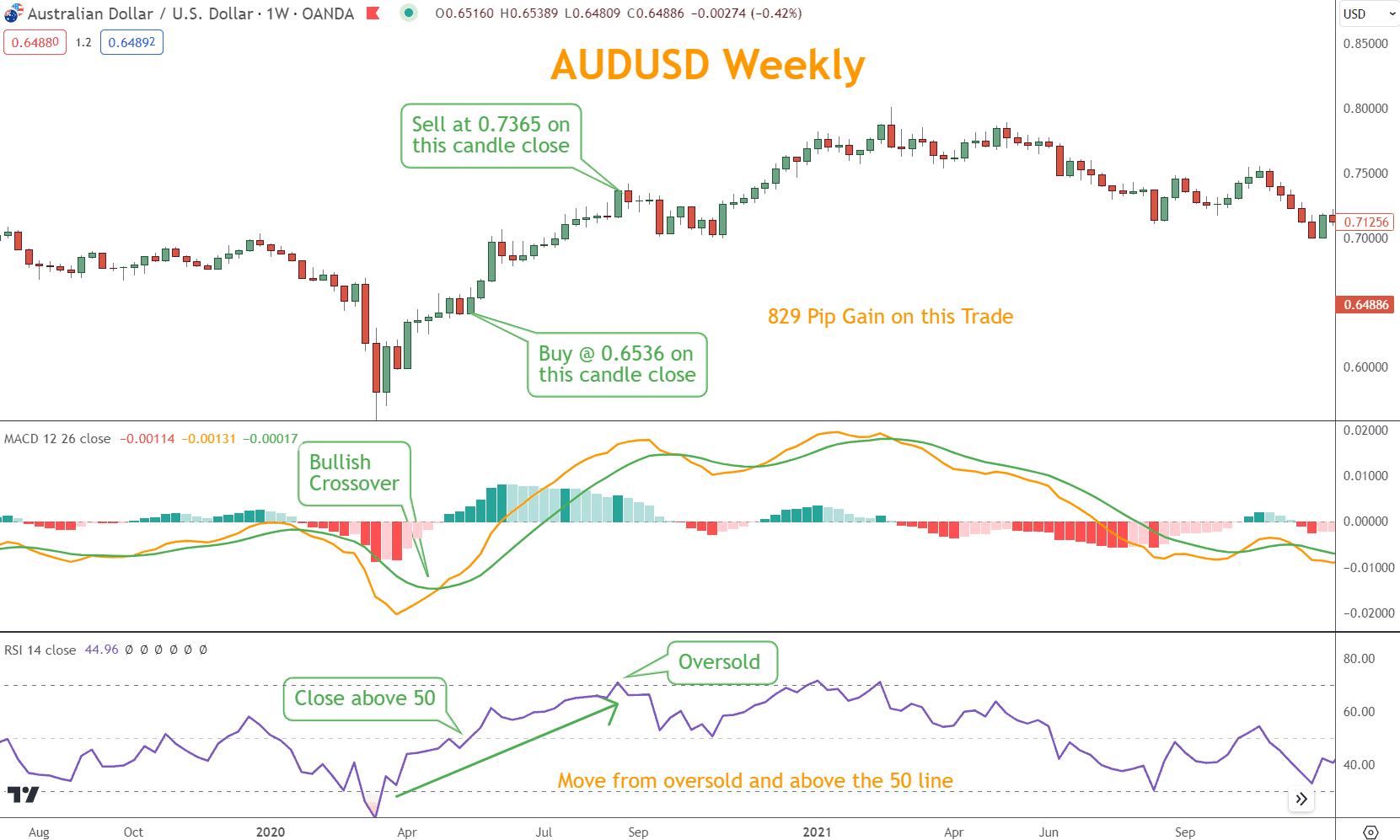
In the first example below using AUD/USD, the MACD achieves a bullish crossover on 04/27/20, indicating the trend is now Bullish.
Meanwhile, the RSI moved higher from oversold territory, and 05/18/20 crossed the 50 line, providing Bullish confirmation and a buy signal.
AUDUSD moved higher with little interruption, and on 08/24/20, the RSI registered an oversold reading.
An oversold reading on a Bullish candlestick is an excellent reason to take profit and, with it, gain 829 pips.
This is a textbook perfect trade because the MACD found the trend and timed the entry and exit using the RSI momentum methodology.
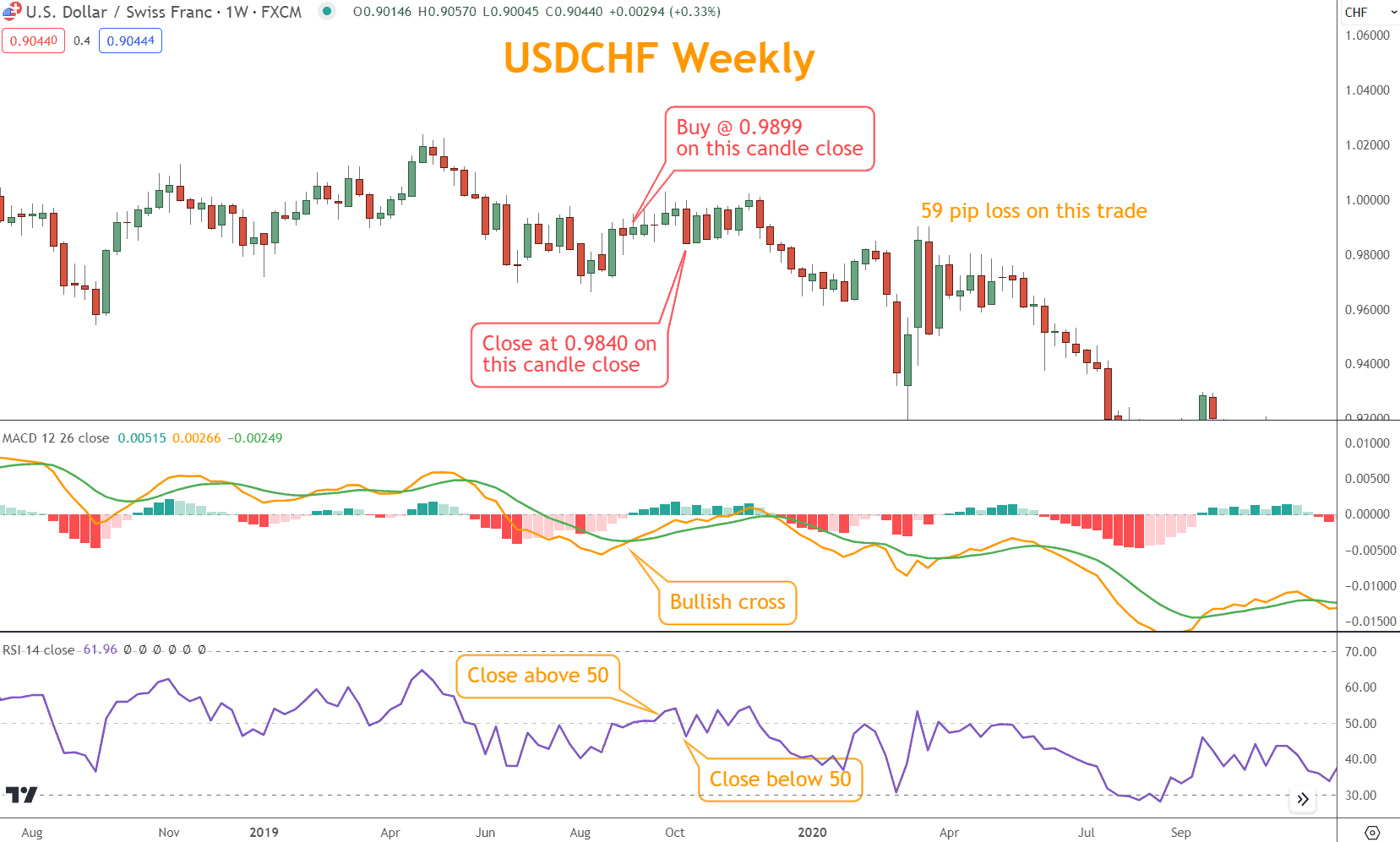
The following example of using USD/CHF shows how these indicators struggle with sideways price action.
In this example, the MACD achieves a Bullish cross on 09/19/19; on the same day, the RSI crosses the 50 line.
Although an oversold position drives the RSI, this coincidence should lead to a winning trade.
Unfortunately, the price action has little momentum, and five weeks later, the transaction closes for a 59 pip loss.
With the benefit of hindsight, it’s easy to rationalize that you would never have opened this trade.
However, if you make trading decisions based on rules, you must consider every trade.
Even though the loss is slight, this situation exposes a limitation of this strategy. Neither the MACD using an exponential moving average nor the RSI handles consolidation well.
The alternative is to enact more extreme rules, such as requiring that every RSI signal recently come from an overbought or oversold condition.
The problem with extreme rules is they yield very few trading opportunities because market conditions are rarely at extremes.
Extreme rules mean you watch the market produce pips while sitting on the sidelines because an exceptional entry never came.
What are Your Next Steps?
If you are interested in using the MACD as a trading strategy, select a favorite Forex pair and use the MACD with and without a complementary indicator, such as the RSI.
Then, consider how you would use these together to find trading opportunities.
I think there are better tools than these and recommend looking elsewhere.
If you need a charting platform, I recommend TradingView. You can start with it here for free. If you open a paid account, we’ll receive a commission.
If you’re new to trading, consider opening a demo account and trading with play money before real money.
If you need help finding trading opportunities, download the Six Basics of Chart Analysis for free here.
The Six Basics will give you a strong foundation in chart analysis, which you can incorporate with what you’ve learned about trends here.
In addition, when you get the “Six Basics,” you’ll also get Forex Forecast delivered to your inbox every Sunday.
Forex Forecast is delivered weekly to your inbox and provides the following:
- Trade Ideas and Analysis
- I will show you the trade opportunities I’m watching using the Six Basics of Chart Analysis and Advanced Strategies.
- Case Studies from Around the Web
- Watch how applying the Six Basics worked on some of the best, most profitable trades.
- Trading Education Guides and Videos
- Want to learn most Six Basics techniques and advanced strategies? I produce videos and guides to help you understand and improve trading practices.
- Links to New Articles
- I publish new articles on topics traders will want to know about every week, and you can find out when they post.
- Positionforex.com News
- Did something change at positionforex.com? Learn about it here first!
- Links to upcoming webinars
- Attend free webinars to improve your trading.
- And Much More
- Tools, Membership-only Videos, and more will be released in the Forex Forecast.
The best part – it’s completely free.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Trading with MACD Work?
Trading with the MACD can work when combined with other technical analysis indicators. However, like any moving average-based indicator, MACD suffers from lagging signals.
However, given the opportunity to integrate with other forms of technical analysis, the MACD could be a valuable part of any trader’s strategy.
What is the MACD, and how is it Calculated?
The MACD is a momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of a security’s price.
It’s calculated by subtracting the 26-period Exponential Moving Average (EMA) from the 12-period EMA, which results in the MACD line.
The nine-day EMA of the MACD, called the “signal line,” is then plotted on top of the MACD line, which can trigger buy and sell signals.
Traders may buy the security when the MACD crosses above its signal line and sell—or short—it when it crosses below it.
What do the MACD Lines Indicate?
The MACD lines indicate momentum and trend direction. When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it means a bullish signal, suggesting it might be a good time to buy.
Conversely, when the MACD line crosses below the signal line, it indicates a bearish signal, suggesting it might be time to sell.
Additionally, the divergence or convergence of the MACD line to price suggests potential market reversals.
For example, if the price is making new highs but the MACD is not, it could indicate weakening momentum and a possible bearish reversal.
How can Traders use the Histogram to make Trading Decisions?
The MACD histogram measures the distance between the MACD line and its signal line.
When the histogram is positive (MACD above the signal line), it signals bullish momentum.
Conversely, when the histogram is negative (MACD below the signal line), it signals bearish momentum.
Traders often look for histogram reversals as early signs of trend changes. A move from negative to positive histogram values can indicate a bullish reversal, whereas a move from positive to negative can signal a bearish reversal.
Additionally, divergence between the histogram and price action is another signal traders watch for; it can indicate potential trend reversals or weakening momentum.