Forex trading—short for foreign exchange trading—is the buying and selling of currencies to profit from changes in exchange rates.
The Forex market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. According to the Bank for International Settlements (via Reuters), daily trading volume exceeded $7.5 trillion in 2022.
That scale exists because Forex is a global, decentralized market that operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, and includes banks, governments, corporations, hedge funds, and individual traders.
This guide explains Forex trading from the ground up. You’ll learn how the market works, the terminology you must understand, how trades are executed, and which trading approaches are most realistic for beginners—especially those interested in position trading.
TL;DR
Forex trading is not gambling or a shortcut to wealth.
It is a skill-based market that rewards education, discipline, and risk control.
- Forex trades currencies in pairs, driven by macroeconomic forces
- Leverage magnifies both gains and losses—less is better
- Risk management determines survival, not strategy
- Position trading is the lowest-risk approach for most traders
- Long-term success depends on structure, patience, and consistency
Key Forex Trading Terms Every Beginner Must Know
Understanding terminology removes confusion and prevents costly mistakes.
Currency Pairs
Forex trades currencies in pairs. The base currency comes first, and the quote currency comes second.
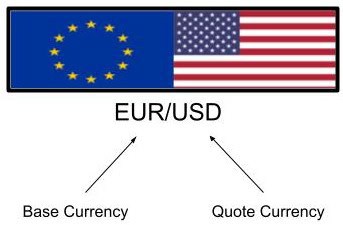
Example: EUR/USD
- EUR = base currency
- USD = quote currency
The exchange rate tells you how many units of the quote currency are needed to buy 1 unit of the base currency.
Exchange Rate
The exchange rate is the price of one currency in terms of another.
If EUR/USD is trading at 1.2000, one euro equals $1.20.
Rates change constantly based on supply, demand, interest rates, economic data, and geopolitical events.
Pip
A pip is the standard unit used to measure price movement.
- Most pairs: 0.0001
- Example: 1.2000 → 1.2001 = 1 pip

Some platforms show “pipettes” (a fifth decimal). These are largely irrelevant for sustainable trading.
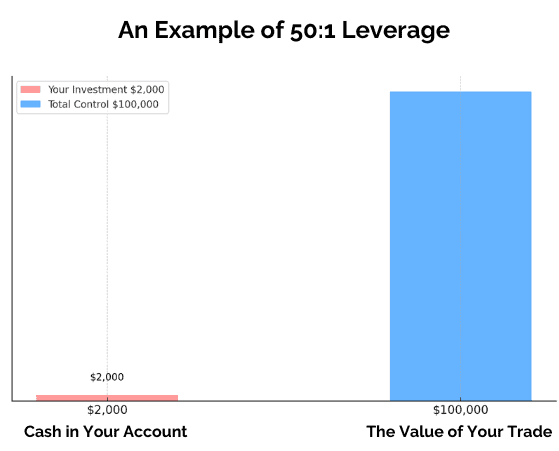
Leverage
Leverage allows you to control a larger position with less capital.
- 50:1 leverage = $1,000 controls $50,000
- U.S. max: 50:1
- EU max: 30:1
Most successful traders use 10:1 leverage or less.
Spread
The spread is the difference between the bid (sell) and ask (buy) price.
Example:
- Bid: 1.1998
- Ask: 1.2000
- Spread: 2 pips

The spread is a trading cost.
Margin
Margin is the capital required to open a leveraged position.
A 1% margin on a $100,000 position requires $1,000.
Poor margin management leads to margin calls and forced liquidation.
Lot Size
A lot is a standardized unit of measurement for trade size in Forex.
Most retail Forex brokers size trades in micro lots; however, always check with your broker for details regarding their platform.
| Lot Type | Units |
| Standard | 100,000 |
| Mini | 10,000 |
| Micro | 1,000 |
Lot size directly affects risk.
How Forex Trades Are Executed (High-Level)
Forex trading is decentralized.
Prices come from a network of liquidity providers—banks and institutions—aggregated by brokers. Retail traders access this liquidity through trading platforms.
Your broker does not “set” prices. It routes your order to available liquidity and earns via spreads, commissions, or both.
Choosing a Trading Platform: TradingView vs MetaTrader
For charting and analysis, TradingView is superior—especially for position traders.
Why TradingView stands out:
- Web-based and device-synced
- Clean charts with superior visibility
- Advanced alerts and custom timeframes
- Platform-independent analysis
MetaTrader (MT4/MT5) is broker-tied and designed around automation.
Automated trading and Expert Advisors are not aligned with position trading and have a poor long-term success record.

Looking for a Strategy?
Download the Six Basics of Chart Analysis and sign up for Forex Forecast to learn a bottom-up approach to analyzing Forex markets and weekly market updates.
How to Open and Close a Forex Trade (Simplified)
- Analyze context (trend, structure, fundamentals)
- Define risk (1–2% per trade)
- Choose position size
- Enter trade manually
- Monitor—not micromanage
- Exit intentionally
- Journal the result
Execution is simple. Discipline is not.
Basic Forex Trading Styles Compared
| Style | Time Horizon | Risk Profile | Recommendation |
| Day Trading | Minutes–hours | Very high | Not recommended |
| Swing Trading | Days | High | Conditional |
| Position Trading | Weeks–months | Lowest | Recommended |
Position trading allows you to:
- Trade less frequently
- Avoid intraday noise
- Use fundamentals properly
- Reduce emotional pressure
What Moves Currency Prices?
Currencies move because of macro forces, not indicators.
| Category | Macro Driver | What It Influences | Why It Moves Currencies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monetary Policy | Interest rates | Capital flows and yield differentials | Higher rates attract capital; lower rates push it away |
| Price Stability | Inflation | Purchasing power and policy response | Rising inflation erodes value and forces central bank action |
| Economic Growth | GDP & labor data | Confidence in economic strength | Strong growth supports currency demand |
| Policy Direction | Central bank policy | Market expectations and forward guidance | Signals future rate paths and liquidity conditions |
| Geopolitics | Political stability | Risk perception and investment flows | Stability attracts investment; uncertainty drives capital out |
| Trade & Supply | Commodity prices | Export revenues and terms of trade | Commodity-linked currencies rise or fall with prices |
Technical analysis helps with timing—but fundamentals drive direction.
Risk Management Is the Strategy
Risk management determines whether you survive long enough to learn.
| Category | Principle | What It Means in Practice | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Mindset | Survival over profits | The primary goal is staying in the game long enough to build skill | Most traders fail due to capital loss, not a lack of strategy |
| Risk Per Trade | Risk 1–2% per trade | Limit losses on any single trade to a small, predefined portion of capital | Prevents one mistake from causing account damage |
| Leverage Control | Use modest leverage | Keep leverage low to avoid amplified losses during volatility | High leverage accelerates drawdowns and emotional mistakes |
| Trade Frequency | Avoid overtrading | Only trade high-quality setups that meet your plan criteria | Excess trades increase costs, errors, and emotional fatigue |
| Portfolio Exposure | Diversify exposure | Spread risk across multiple pairs or themes rather than one position | Reduces impact of adverse moves in a single market |
| Capital Priority | Protect capital first | Focus on defense before growth in all trading decisions | Most traders fail due to capital loss, not lack of strategy |
Position trading allows wider stops and smaller sizing—making risk easier to control.
Why Position Trading Works for Most Traders
Position trading aligns with how markets actually move.
| Aspect | Why It Matters | Practical Benefit for Traders |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction costs | Fewer trades mean fewer spreads and commissions | More profit retained over time |
| Time commitment | Positions are managed on higher timeframes | Minimal screen time required |
| Emotional pressure | Less exposure to intraday noise | Improved decision-making and discipline |
| Fundamental alignment | Trades reflect macroeconomic trends | Stronger conviction and trade longevity |
| Execution discipline | Fewer, higher-quality decisions | Easier consistency and rule adherence |
This is the approach used by institutions—and the one most retail traders overlook.
Conclusion
Forex trading rewards preparation, patience, and restraint—not speed or prediction.
Success comes from understanding how the market works, controlling risk, and choosing a trading style that fits real life.
For most traders, position trading offers the most straightforward path to consistency.
What’s the Next Step?
Evaluate your trading approach honestly:
- Are you trading too frequently?
- Are emotions driving decisions?
- Are you reacting—or planning?
If you want a position-trading framework that works across all markets and platforms, start with the Six Basics of Chart Analysis.
They keep your focus on price, structure, and context—the foundation of long-term trading success.
Forex Trading 101 Quiz
1. What is Forex trading primarily concerned with?
A. Stocks
B. Commodities
C. Currencies
D. Bonds
2. What does leverage do?
A. Reduces spreads
B. Increases trade frequency
C. Controls larger positions with less capital
D. Eliminates risk
3. Which trading style has the lowest risk profile?
A. Scalping
B. Day trading
C. Swing trading
D. Position trading
4. What primarily drives long-term currency trends?
A. Indicators
B. Chart patterns
C. Economic fundamentals
D. Broker pricing
5. Why is risk management critical?
A. It improves win rate
B. It guarantees profits
C. It prevents catastrophic losses
D. It replaces analysis
Answer Key
- C
- C
- D
- C
- C
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Forex Trading?
Forex trading, or foreign exchange trading, involves buying and selling currencies to profit from changes in their exchange rates.
Traders speculate on the price movements of currency pairs, such as EURUSD, in a highly liquid and continuously operating global market.
How Does Leverage Work in Forex Trading?
Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital.
For example, with 50:1 leverage, a trader can control $50,000 with just $1,000.
While leverage can amplify profits, it also increases the potential for significant losses, making risk management crucial.
What Is a Pip in Forex Trading?
A pip, short for “percentage in point,” is the smallest price movement in the exchange rate of a currency pair. For most currency pairs, a pip is equal to 0.0001.
Pips are used to measure price changes and calculate profits or losses in forex trading.
Why Should I Use a Demo Account Before Trading with Real Money?
A demo account allows traders to practice forex trading without risking real money.
It helps them become familiar with the trading platform, test strategies, and gain confidence in their trading skills.
This preparation is essential for reducing mistakes and improving performance when trading live.
Forex Trading Disclosure Statement
Risk Warning:
Forex trading involves significant risk and may not be suitable for all investors. The leveraged nature of Forex trading can work both for and against you, leading to substantial gains or losses. Before trading Forex, you should carefully consider your financial objectives, experience level, and risk tolerance. It is possible to lose more than your initial investment, and you should only trade with money you can afford to lose.
Market Risks and Volatility:
Forex markets are influenced by global economic, political, and social events, which can result in unpredictable price movements. High market volatility can lead to sudden and substantial changes in currency values, potentially causing losses that exceed your initial deposit.
Leverage Risks:
Leverage amplifies both potential gains and potential losses. While leverage can increase profitability, it also increases the risk of significant losses, including the loss of your entire trading capital.
Trading Tools and Technology Risks:
Forex trading platforms, including those offered by brokers, are subject to technology risks, such as system failures, latency issues, and potential errors in price feeds. Traders should be aware that these risks can impact the execution of trades and trading outcomes.
No Guarantee of Profitability:
Past performance in Forex trading is not indicative of future results. There is no guarantee that you will achieve profits or avoid losses when trading Forex. Market conditions and individual trading strategies vary, and no trading system can eliminate the inherent risks of Forex trading.
Educational Purposes Only:
Any information provided about Forex trading, including strategies, analysis, or market commentary, is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Consult a qualified financial advisor or tax professional before making any trading decisions.
Regulatory Compliance:
Forex trading is regulated differently in various jurisdictions. Ensure that you are trading with a broker that is licensed and compliant with regulations in your country of residence.
Responsibility:
You are solely responsible for your trading decisions and the risks associated with them. It is your duty to understand the terms and conditions of Forex trading, including margin requirements, stop-losses, and other risk management tools.
Acknowledgment:
By engaging in Forex trading, you acknowledge that you have read, understood, and accepted this disclosure statement. You accept full responsibility for the outcomes of your trading decisions and agree to trade at your own risk.
This disclosure is intended to provide an overview of the risks associated with Forex trading and is not exhaustive. For additional information, consult your broker and other reliable financial resources.


